Carbon Dioxide vs. Carbon Monoxide: Understanding the Silent Killer
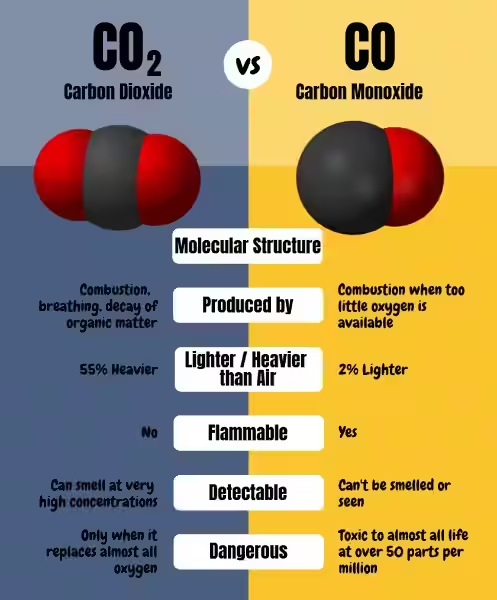
Carbon dioxide (CO2) and carbon monoxide (CO) are often confused, leading to misinterpretations and even potentially dangerous situations. Both gases are colorless, odorless, and tasteless, but their chemical makeup and effects on human health differ significantly. Understanding the distinctions between these two gases is vital for ensuring safety and making informed decisions about gas detection systems.
The Chemical Difference: A Tale of Two Molecules
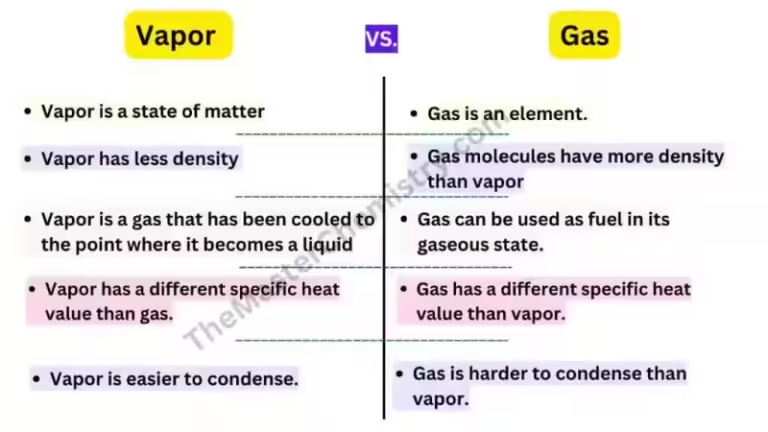
The difference between CO and CO2 lies in their molecular composition. Carbon dioxide (CO2) is formed by one carbon atom bonded to two oxygen atoms, while carbon monoxide (CO) consists of one carbon atom bonded to one oxygen atom. This seemingly simple difference results in drastically different properties and consequences.
CO2: The Gas of Life and Climate Change
Carbon dioxide is a natural component of Earth's atmosphere, playing a crucial role in the planet's climate and the survival of plant life. Plants use CO2 during photosynthesis to create energy, making it a vital part of the natural carbon cycle. However, the increasing concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere due to human activities, primarily the burning of fossil fuels, is a significant contributor to global warming.
CO: The Silent Killer
Unlike CO2, carbon monoxide is not naturally present in the atmosphere. This gas is a byproduct of incomplete combustion, occurring when fuels like wood, gas, and oil do not burn completely due to insufficient oxygen. This incomplete burning releases CO, a highly toxic gas that can be deadly even in small concentrations.
Health Hazards: A Battle Between Life and Death
The health risks posed by CO2 and CO are vastly different. While CO2 is generally safe in small amounts, high concentrations can cause oxygen displacement and lead to suffocation. Symptoms of CO2 exposure include headaches, dizziness, and confusion. In extreme cases, it can be fatal.
CO2: A Suffocating Threat
High concentrations of CO2 in enclosed spaces can be dangerous, especially in areas with poor ventilation. This is why it's crucial to ensure proper ventilation in places like industrial settings, breweries, or greenhouses where CO2 levels may be elevated.
CO: A Silent and Deadly Poison
Carbon monoxide is a far more dangerous threat, earning the moniker "Silent Killer" due to its inability to be detected by human senses. When inhaled, CO binds to hemoglobin in the blood, preventing oxygen from reaching vital organs. This can lead to a slow and painful suffocation, causing various symptoms like headaches, dizziness, nausea, weakness, and even death.
Avoiding the Silent Killer: Choosing the Right Gas Detection System
The differences in properties and health risks between CO and CO2 necessitate the use of specific gas detection systems tailored to the environment and potential hazards. Understanding these differences is crucial for choosing the right equipment to protect human life.
CO2 Detection: Keeping a Safe Environment
CO2 detectors are typically used in areas where high levels of CO2 may accumulate, such as industrial settings, breweries, or greenhouses. These detectors monitor CO2 levels and alert personnel when levels become dangerous.
CO Detection: Protecting Against the Silent Killer
CO detectors are essential in areas where incomplete combustion can occur, such as homes with gas appliances, garages, or industrial workshops. These detectors are specifically designed to detect CO and trigger an alarm when levels reach a dangerous threshold.
It is important to note that CO detectors do not measure CO2 levels, and vice versa. You need separate detectors for each gas to ensure adequate safety measures.
Conclusion: Understanding the Differences for Safety
While often confused, CO2 and CO are distinct gases with stark differences in their properties and health risks. It's crucial to understand these distinctions to select the appropriate gas detection system and ensure a safe and healthy environment. By taking the necessary precautions and choosing the right detection equipment, you can protect yourself and your loved ones from the dangers of CO and CO2 exposure.
Frequently Asked Questions About CO and CO2
What is the difference between CO and CO2?
CO2 (carbon dioxide) is a product of complete combustion, where hydrocarbons react with oxygen to produce CO2 and water. It's a natural component of Earth's atmosphere, essential for plant life. CO (carbon monoxide), however, is formed during incomplete combustion due to limited oxygen availability. It's not naturally present in the atmosphere.
What are the health risks associated with CO and CO2?
CO2 is generally safe as a byproduct of respiration. High concentrations can cause suffocation due to oxygen displacement and lead to headaches and dizziness. CO, on the other hand, is dangerous at any concentration. It binds to hemoglobin, preventing oxygen transport to tissues, leading to slow suffocation. Symptoms include headache, dizziness, and nausea.
How do I choose the right gas detection system for my needs?
The appropriate gas detection system depends on the specific environment and potential hazards. CO2 detectors are suitable for areas where high levels of CO2 can accumulate, such as industrial settings, breweries, or greenhouses. CO detectors are essential in areas where incomplete combustion can occur, like garages, homes with gas appliances, or industrial workshops.