Understanding Your Household Electricity Consumption: A Guide to kWh and Savings
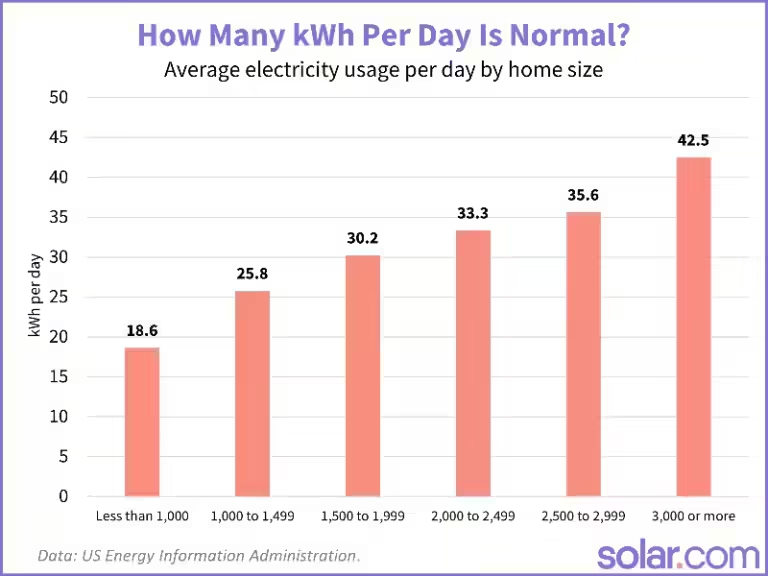
Have you ever wondered how much electricity your household uses each day? You're not alone. Understanding your energy consumption is vital for making informed decisions about your energy bills and environmental impact. The average American household uses about 30 kWh per day, totaling 10,800 kWh annually. This translates to roughly 900 kWh per month.
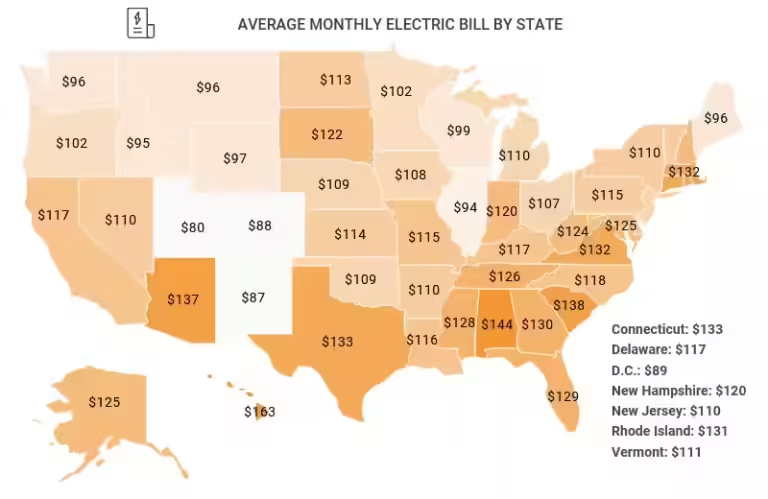
However, this average varies greatly across the US, with southern households using nearly 37 kWh per day and northeastern households using just 22 kWh per day. Let's explore the factors that influence your household's electricity usage and how you can reduce your consumption, saving both money and the environment.
Factors Influencing Electricity Consumption
Several factors contribute to the amount of electricity your home consumes. Understanding these factors can help you pinpoint areas where you can make changes to reduce your overall usage.
1. Electricity Costs
Higher electricity prices encourage conservation. States with the highest electricity costs tend to have lower average household consumption. For example, Hawaii, with the highest electricity prices, consumes the least electricity per household, while Louisiana, with the lowest prices, consumes the most.
2. Climate
Air conditioners, primarily powered by electricity, contribute to higher electricity usage in warmer climates. Southern states with hot summers typically have higher average daily kWh consumption than those in cooler climates.
3. Home Size
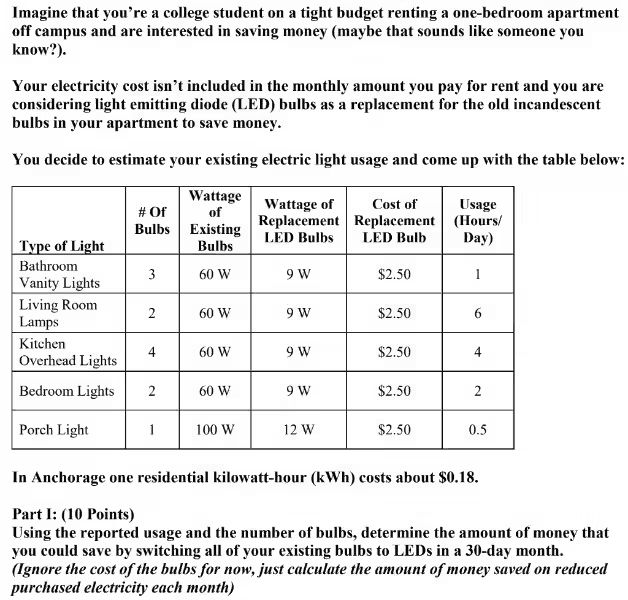
Larger homes require more energy for heating, cooling, and lighting. A 3,000 square foot home uses more than double the electricity of a 1,000 square foot home. The size of your home directly influences your overall energy needs.
4. Household Size
Larger families tend to use more appliances and, therefore, consume more electricity. Even though individual appliances don't consume a significant amount of energy, the cumulative effect of multiple appliances used by a larger family can significantly increase overall consumption.
5. Home Construction
Building materials impact insulation and heat transfer. Wood and brick are poor conductors, while glass is an excellent conductor. Homes with well-insulated walls and roofs can maintain comfortable temperatures with less energy expenditure.
6. Home Orientation
Homes receiving ample sunlight require less artificial lighting and are easier to heat in winter, but harder to cool in summer. Careful consideration of your home's orientation can significantly impact your heating and cooling needs.
7. Roofing
Light-colored roofs reflect sunlight, reducing heat absorption and cooling costs. Darker roofs absorb more heat, increasing the energy required to keep your home cool during the summer months.
8. Insulation
Proper insulation in walls, roofs, and floors minimizes heat transfer and saves energy. Insulation acts as a barrier, preventing heat loss in the winter and heat gain in the summer, reducing the strain on your heating and cooling systems.
9. Building Envelope
An airtight envelope prevents energy loss through gaps and cracks, reducing heating and cooling cycles. A well-sealed envelope minimizes air leakage, ensuring that your heating and cooling systems efficiently maintain the desired temperature.
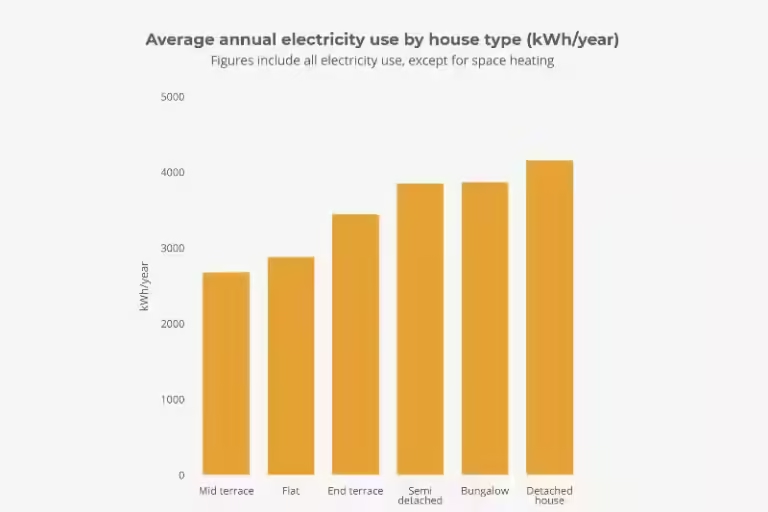
10. Household Appliances
Space heaters, water heaters, and air conditioners account for over 40% of household electricity usage. Newer appliances tend to be more energy efficient. Choosing energy-efficient appliances can significantly reduce your electricity consumption and save money on your energy bills.
Lowering Your kWh Consumption
Reducing your household's average daily kWh consumption not only saves money but also contributes to a more sustainable environment. Here are some strategies to lower your electricity usage:
1. Monitor Energy Habits
Identify areas for improvement, like running appliances when half-full or leaving lights on unnecessarily. Making conscious choices about your energy usage can lead to significant savings.
2. Unplug "Energy Vampires"
Devices like tablets and gaming consoles draw energy even when turned off, contributing to higher energy bills. Unplug these devices when not in use to reduce phantom energy consumption.
3. Run Appliances During Off-Peak Hours
Electricity prices fluctuate; use appliances during cheaper off-peak hours. Many utility companies offer time-of-use pricing, allowing you to save money by running energy-intensive appliances during cheaper times.
4. Switch to ENERGY STAR Appliances
These appliances use less energy while maintaining performance, saving money in the long run. ENERGY STAR certified appliances are designed to be more energy-efficient, translating to lower electricity bills and reduced environmental impact.
5. Install LEDs
LEDs last longer and consume less electricity than traditional bulbs. Switching to LED lighting can significantly reduce your lighting energy consumption and save money on replacements.
6. Service Your Air Conditioner
Regular maintenance ensures optimal performance and reduces energy consumption. A well-maintained air conditioner operates efficiently, using less energy to keep your home cool.
7. Consider a Home Energy Audit
A professional audit provides detailed recommendations for improving efficiency and reducing energy consumption. An energy audit can identify areas for improvement and offer tailored solutions to reduce your electricity usage.
Beyond Saving Energy
Reducing your electricity consumption is an important step towards a greener future. However, it's also essential to protect your home's electrical system to ensure reliable power and prevent costly repairs.
1. Protect Your Home's Electrical System
Regular maintenance and protection from wear and tear are crucial for reliable power and preventing costly repairs. Consider a home warranty program to cover potential issues.
By understanding the factors influencing your electricity consumption and implementing energy-saving strategies, you can reduce your average kWh per day, save money on your energy bills, and contribute to a more sustainable future. Remember, every kilowatt-hour saved makes a difference!
Frequently Asked Questions about Average Daily Kilowatt Hours
What is the average daily kilowatt-hour (kWh) usage for a US household?
The average American household uses about 30 kWh per day.
How much does the average US household use per month?
The average monthly consumption is around 900 kWh.
Does the average daily kWh usage vary by location?
Yes, the average daily kWh usage varies significantly based on location, home size, and family size. Southern states average around 37 kWh per day, while the Northeast and West average around 23 kWh per day.
What factors influence daily kWh consumption?
Factors like climate, home size, household size, home construction, home orientation, roofing, insulation, building envelope, and household appliances all affect daily kWh consumption.