The Oxygen in Earth's Atmosphere Was Released By... Cyanobacteria!

The Transformation of Earth’s Atmosphere
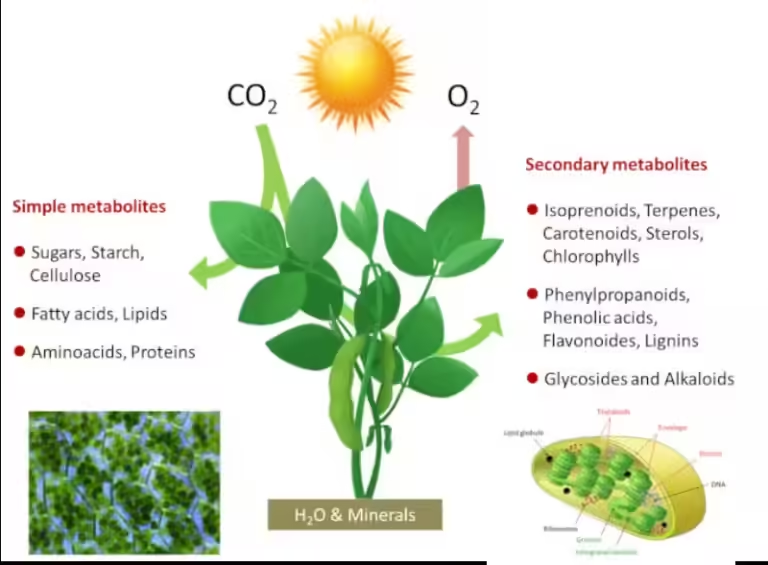
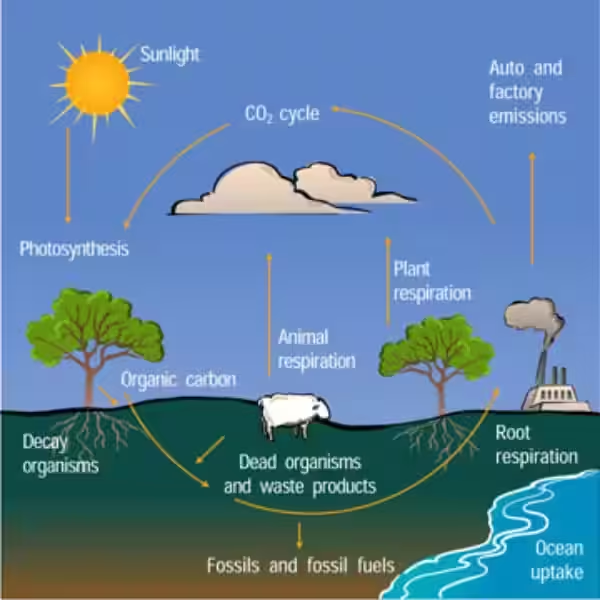
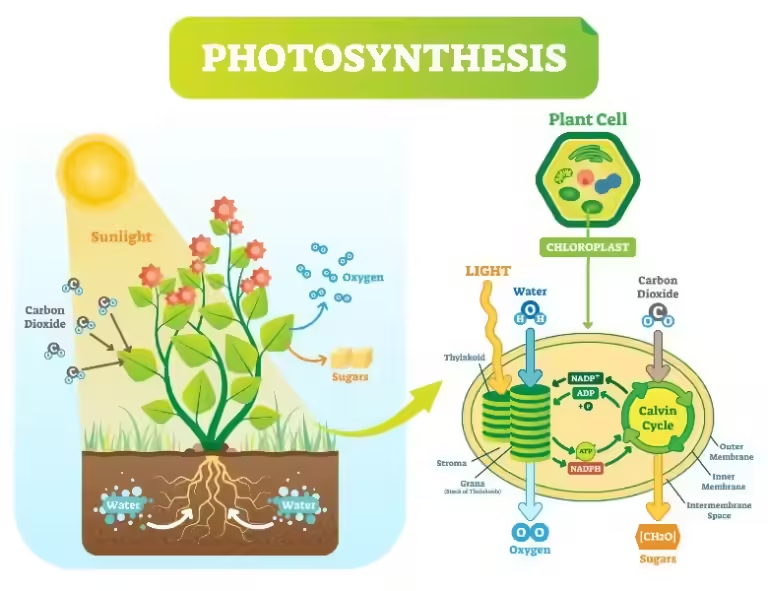
Imagine a world without oxygen, a world where the air we breathe is a toxic mix of gases. This was the reality for billions of years on Earth. But then, something extraordinary happened. Tiny, single-celled organisms called cyanobacteria, also known as blue-green algae, evolved the ability to perform photosynthesis. This simple act of using sunlight to create energy, with oxygen as a byproduct, changed the face of our planet forever.
Cyanobacteria were the first organisms to release oxygen as a byproduct of photosynthesis. Prior to their emergence, the atmosphere was primarily composed of carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrogen. The oxygen released by cyanobacteria reacted with other elements, particularly iron, which was abundant in the ancient oceans. This resulted in the formation of iron oxide, which precipitated out of the oceans, forming layers of iron-rich rock.
The Great Oxidation Event: A Turning Point in Earth’s History
Around 2.45 billion years ago, a critical threshold was reached. Oxygen levels in the atmosphere began to rise dramatically, marking a period known as the Great Oxidation Event. This event was a watershed moment in Earth's history, fundamentally altering the planet's chemistry, climate, and the course of evolution.
The Great Oxidation Event had several profound consequences:
- The Rise of Aerobic Life: Many early life forms, unable to tolerate oxygen, perished in the toxic environment. However, this event also paved the way for the evolution of aerobic organisms, which evolved mechanisms to utilize oxygen for energy production. This new type of metabolism was far more efficient than the anaerobic metabolism that dominated the early Earth, leading to the diversification of life.
- The Formation of the Ozone Layer: Oxygen in the atmosphere reacted with ultraviolet radiation from the sun, forming a protective layer of ozone. This layer shields Earth from harmful radiation, making it possible for life to thrive on land.
- Climate Change: Oxygen replaced methane, a potent greenhouse gas, causing a cooling effect on the planet. This may have contributed to one of the earliest ice ages.
The Mystery of the “Boring Billion”
Following the Great Oxidation Event, a period known as the "boring billion" occurred. This period, lasting from about 2.5 billion to 1.5 billion years ago, saw relatively stable oxygen levels. However, the reasons for this stability, and why oxygen levels did not rise to support more complex life forms, remain a mystery.
The Continuing Evolution of Earth’s Atmosphere
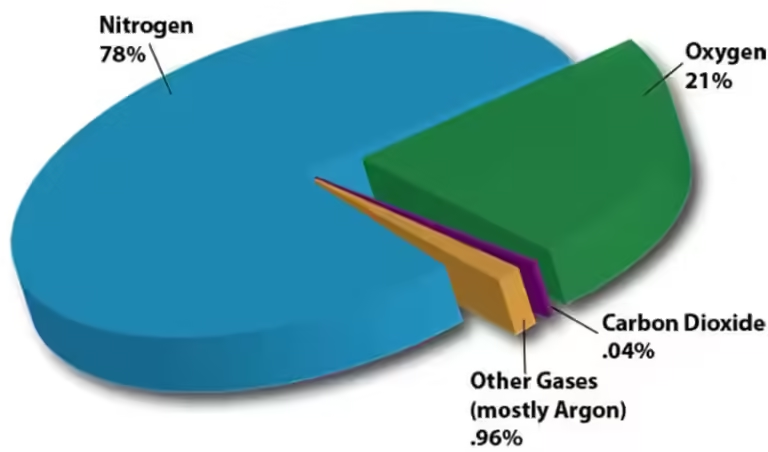
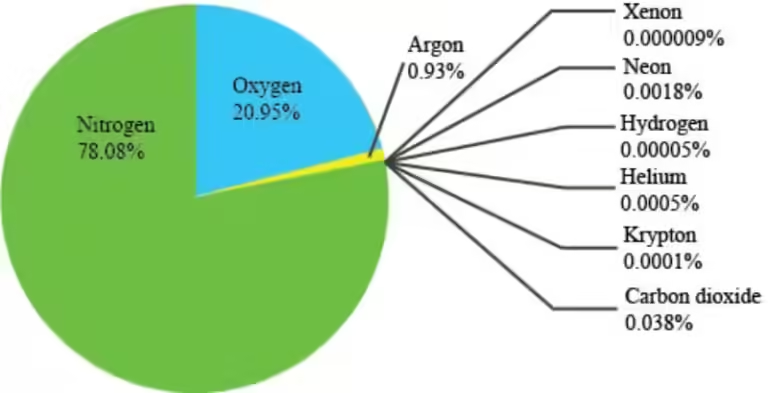
While the Great Oxidation Event was a pivotal moment, Earth's atmosphere continues to evolve. Volcanic activity, plate tectonics, and even the respiration of plants and animals influence oxygen levels. The modern atmosphere, with its 21% oxygen content, is a product of this continuous interplay of natural processes.
The Legacy of Cyanobacteria
The oxygen in the air we breathe, the ozone layer that shields us from the sun's harmful rays, and the diversity of life on Earth can all be traced back to the humble cyanobacteria. These tiny microbes, through their ability to photosynthesize, fundamentally changed the course of evolution, making possible the complex life forms that we see today. Their legacy is a testament to the power of life to shape the planet we call home.
Frequently Asked Questions:
What released the oxygen in Earth's atmosphere?
Cyanobacteria, also known as blue-green algae, were responsible for releasing oxygen into the atmosphere through photosynthesis.
When did the oxygen in the atmosphere start to accumulate?
Oxygen production by cyanobacteria likely began around 2.7-2.8 billion years ago. However, it took millions of years for oxygen to accumulate in the atmosphere, leading to the Great Oxidation Event around 2.45 billion years ago.
What is the Great Oxidation Event?
The Great Oxidation Event marks a significant shift in Earth's atmosphere, when oxygen levels dramatically increased, transforming the planet's chemistry, climate, and the course of life.
How did the Great Oxidation Event impact life on Earth?
The rise of oxygen led to the extinction of many anaerobic life forms that could not tolerate oxygen. However, it also paved the way for the evolution of aerobic metabolism, which utilizes oxygen to generate energy more efficiently. This ultimately led to the diversification of life.
What is the role of photosynthesis in oxygen production?
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants and cyanobacteria use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to produce energy and release oxygen as a byproduct.