Understanding Solar Energy: The Sequence of Operation, Pros, and Cons

Harnessing the power of the sun to generate electricity has become increasingly popular, with homeowners and businesses alike seeking to reduce their carbon footprint and energy bills. This article delves into the fascinating world of solar energy, exploring the sequence of operations in a typical solar energy system and highlighting its benefits and drawbacks.
The Journey of Sunlight: A Step-by-Step Guide
Imagine a ray of sunlight striking a solar panel. The journey to converting that light into usable electricity involves several crucial steps:
1. Solar Panel Energy Generation
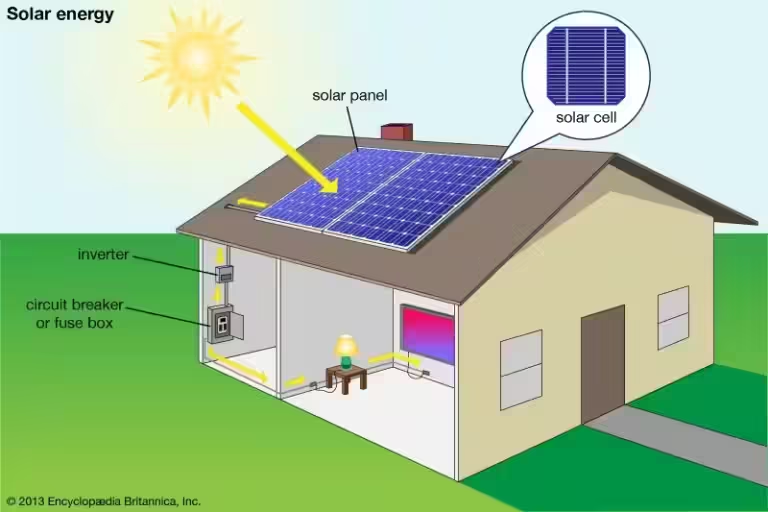
The heart of any solar energy system is the photovoltaic (PV) panel. These panels are made up of multiple solar cells, which are essentially semiconductors that absorb sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity. The energy conversion process is based on the photoelectric effect, where photons from sunlight excite electrons in the semiconductor material, creating an electrical current.
2. DC to AC Conversion: The Role of the Inverter
The DC electricity generated by the solar panels is not directly compatible with household appliances or the electrical grid, which primarily use alternating current (AC) electricity. This is where the inverter comes into play. The inverter acts like a transformer, converting the DC electricity from the solar panels into AC electricity.
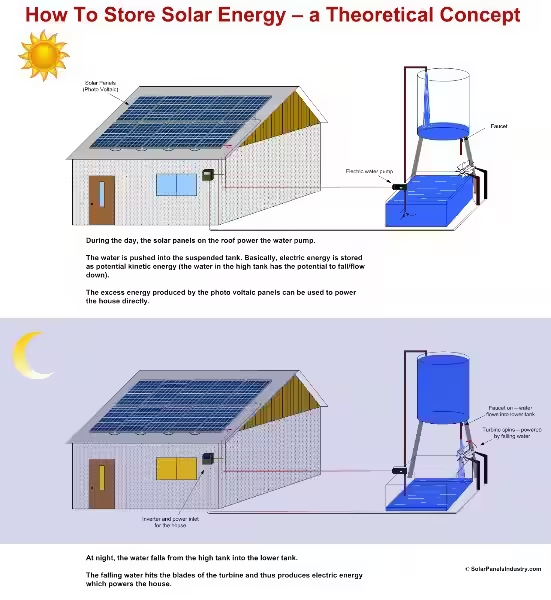
3. Energy Storage and Management: The Importance of Batteries
While solar panels generate electricity during daylight hours, sunlight is not always available, especially during nighttime or cloudy weather. To ensure a continuous energy supply, batteries can be used to store excess AC electricity generated during the day. These batteries can then release the stored electricity when needed, providing power even when the sun isn't shining.
A crucial component in the storage system is the charge controller. This device acts as a gatekeeper, regulating the flow of electricity between the solar panels, batteries, and the load. The charge controller prevents the batteries from overcharging, which can damage them, and from deep discharging, which can shorten their lifespan.
4. Electricity Use and Grid Integration: Powering Your Home and Beyond
The AC electricity produced by the inverter can be used directly to power appliances and devices in your home or business. If you generate more electricity than you need, you can choose to feed the excess back into the electrical grid. This process, known as net metering, allows you to sell your surplus energy to the utility company, potentially offsetting your electricity bill.
5. System Monitoring and Maintenance: Ensuring Efficiency and Longevity
To maximize the performance and lifespan of your solar energy system, regular monitoring and maintenance are essential. Modern systems come equipped with monitoring software that allows you to track energy production, consumption, and system performance in real time. This data helps identify potential issues early on, reducing the risk of downtime.
Maintenance tasks include cleaning the solar panels to remove dirt and debris that can hinder sunlight absorption, and inspecting the system components for any signs of wear or damage. Regular maintenance ensures optimal efficiency and extends the lifespan of your solar energy system.
The Bright Side of Solar Energy: Unlocking its Potential
Solar energy offers numerous advantages, making it an attractive choice for individuals and businesses seeking clean and sustainable energy solutions:
1. Efficiency Optimization: Maximum Output from Every Ray of Sunlight
Solar energy systems are designed for maximum efficiency, utilizing every ray of sunlight to generate power. Advancements in solar panel technology and inverter design have significantly increased energy conversion rates, making solar energy even more efficient.
2. Energy Independence: Breaking Free from the Grid
By generating your own electricity, you can reduce your reliance on the electrical grid, becoming less susceptible to power outages and fluctuations in energy prices. This independence can be particularly valuable in areas prone to grid disruptions or those with unreliable electricity supply.
3. Cost Savings: Lower Energy Bills and Potential Rebates
Perhaps the most compelling advantage of solar energy is the potential for significant cost savings. Reduced electricity bills and credits for excess energy fed back into the grid can lead to substantial financial benefits over time. In many regions, government incentives and tax credits are available to further reduce the initial investment in solar energy systems.
4. Environmental Benefits: A Clean and Renewable Energy Source
Solar energy is a clean and renewable energy source that does not produce greenhouse gas emissions, unlike fossil fuels. By reducing our dependence on traditional energy sources, solar energy contributes to a healthier environment and mitigates the effects of climate change.
5. Scalability and Flexibility: Adapting to Changing Energy Needs
Solar energy systems are modular, meaning they can be easily expanded as your energy needs grow. This flexibility allows you to start small and gradually increase the size of your system to meet your evolving energy demands.
6. Advanced Monitoring and Control: Real-time Insights for Optimization
Modern solar energy systems offer real-time data monitoring and control capabilities. You can track your energy production, consumption, and system performance in detail, allowing you to identify areas for optimization and make informed decisions about your energy usage.
The Shadows of Solar Energy: Addressing the Challenges
While solar energy offers numerous benefits, it's essential to acknowledge the challenges associated with its implementation:
1. Initial Cost: A Significant Investment
The upfront cost of installing a solar energy system can be a significant barrier for many, especially considering the investment in panels, inverters, batteries, and professional installation. However, government incentives and financing options can help offset this cost, making solar energy more accessible.
2. Intermittent Energy Production: The Sun Doesn't Always Shine
Solar energy production is dependent on sunlight, meaning it's not a constant energy source. Cloudy days, nighttime, and seasonal variations in sunlight can significantly impact energy generation. Batteries can help mitigate this issue by storing excess energy during sunny days for use when needed, but battery capacity and lifespan are factors to consider.
3. Maintenance and Repair Costs: Ongoing Expenses to Consider
While solar panels require minimal maintenance, occasional repairs and component replacements may be necessary over the system's lifespan. These costs can add up over time, so it's essential to factor them into your long-term budget.
4. Complex Installation Process: Expertise Required for Optimal Results
Proper installation of a solar energy system requires specialized knowledge and expertise. Hiring qualified professionals is crucial to ensure the system is installed correctly and meets safety standards. Improper installation can lead to inefficiencies, safety hazards, and potential warranty issues.
5. Energy Storage Limitations: Balancing Capacity and Cost
Battery storage plays a vital role in mitigating the intermittency of solar energy production, but it comes at a cost. Battery capacity, lifespan, and replacement costs are factors to consider when evaluating the overall cost-effectiveness of a solar energy system.
6. Regulatory and Permitting Challenges: Navigating the Approval Process
Navigating complex regulations and obtaining necessary permits for solar energy projects can be time-consuming and add to the overall cost. Local zoning regulations, building codes, and utility grid interconnection requirements can vary significantly, requiring careful planning and coordination.
The Future of Solar Energy: Innovation and Growth
Despite the challenges, solar energy is a rapidly evolving field with exciting advancements on the horizon:
1. Emerging Technologies: Enhancing Efficiency and Affordability
Continuous innovation in solar panel efficiency, inverter technology, and battery storage is making solar energy systems more powerful, efficient, and affordable. These advancements are paving the way for wider adoption of solar energy as a viable and cost-effective energy source.
2. Smart Grid Integration: Seamless Energy Management
Integrating solar energy systems with smart grids enables better energy management, grid stability, and the efficient utilization of renewable energy sources. Smart grids can optimize energy flow from solar panels to the grid, ensuring reliable and efficient energy distribution.
3. Policy and Incentives: Accelerating the Transition to Solar Energy
Government policies and financial incentives are crucial for increasing the affordability and accessibility of solar energy. Tax credits, rebates, and net metering programs can encourage homeowners and businesses to embrace solar energy, accelerating the transition to a cleaner and more sustainable energy future.
Conclusion: The Power of the Sun, Shaping a Brighter Future
Solar energy offers a compelling solution to our energy challenges, combining environmental responsibility with economic benefits. The sequence of operations in a solar energy system, from sunlight capture to electricity generation and storage, highlights its complex yet efficient nature. While challenges remain, particularly in terms of initial cost and energy storage limitations, advancements in technology, policy support, and increasing public awareness are driving the adoption of solar energy at an unprecedented rate. By embracing the power of the sun, we can create a more sustainable and prosperous future for generations to come.
Frequently Asked Questions about Solar Energy Systems
What is the sequence of operation in a solar energy system?
Sunlight is captured by solar panels and converted into direct current (DC) electricity. This DC electricity is then transformed into alternating current (AC) by an inverter, making it compatible with household appliances. AC electricity can be used immediately, stored in batteries for later use, or fed back into the grid.
What are the main benefits of using solar energy?
Solar energy offers a number of benefits, including:
- Environmental benefits: It's a clean and renewable energy source, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and greenhouse gas emissions.
- Cost savings: Reduced electricity bills and potential credits for surplus energy fed back into the grid can lead to significant cost savings over time.
- Energy independence: It provides a more stable and reliable energy source, especially in areas prone to power outages.
What are the drawbacks of solar energy?
While solar energy offers many advantages, it also has some drawbacks:
- High initial cost: The upfront investment in panels, inverters, batteries, and installation can be significant.
- Intermittent energy production: Solar energy production is dependent on sunlight, meaning it can be inconsistent in cloudy or rainy weather.
- Maintenance and repair costs: While minimal, occasional repairs and component replacements can add to the overall cost over the system's lifespan.
How do I choose between series and parallel connections for solar panels?
The best choice depends on your specific needs:
- Series connections: Offer higher voltage and simplified wiring, ideal for high-voltage applications or systems with limited space.
- Parallel connections: Provide redundancy and voltage tolerance, suitable for off-grid systems or systems with potential shading issues.
What are the future directions for solar energy?
Emerging technologies, smart grid integration, and supportive policies are all working to make solar energy more efficient, affordable, and accessible.