Power Consumption Chart for Electrical Appliances: Unveiling the Hidden Energy Hogs in Your Home
In today's world, we rely heavily on electrical appliances for our daily comfort and convenience. From refrigerators and washing machines to televisions and computers, these devices have become indispensable parts of our lives. However, behind their convenience lies a significant energy cost, often hidden from our view. Understanding how much power each appliance consumes can empower you to make informed decisions about your energy usage and potentially save money on your electricity bills.
This article delves into the world of appliance power consumption, providing a comprehensive guide to help you decipher the energy demands of your household. We'll explore a variety of appliances, from common household staples to less frequently used items, and provide insights into their power consumption. This knowledge, armed with practical tips and strategies, can help you become a more energy-conscious consumer, reducing your environmental impact and lowering your energy bills.
Unveiling the Power Consumption of Common Household Appliances
Understanding the power consumption of your appliances is crucial for effective energy management. Each appliance draws a specific amount of power, measured in watts (W). The higher the wattage, the more energy the appliance consumes. To illustrate this concept, let's consider a simple analogy: imagine a water hose. The larger the hose's diameter, the more water flows through it. Similarly, a higher wattage appliance consumes more electricity.
Understanding the Power Consumption Chart for Everyday Appliances
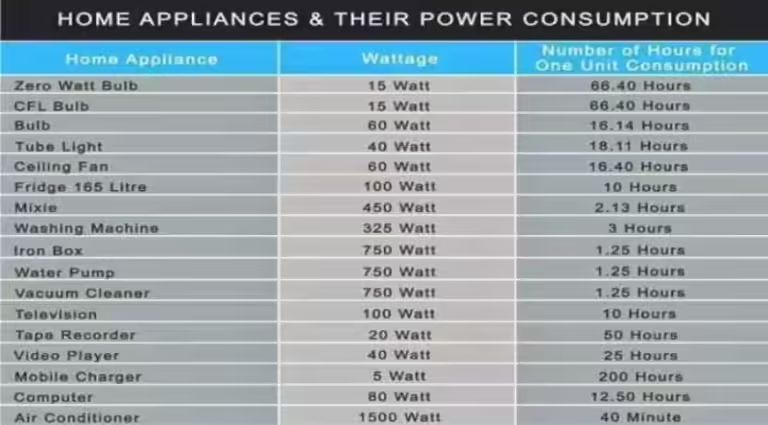
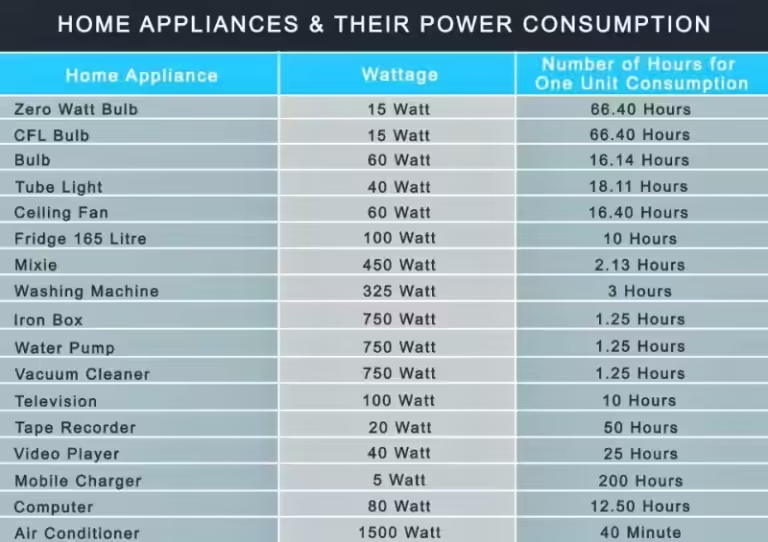
The following table provides a breakdown of the typical wattage for common household appliances, offering a starting point for understanding your appliance's energy use. Remember, these are estimates, and the actual power consumption can vary based on factors such as appliance size, model, and usage habits.
| Appliance | Typical Wattage (W) |
|---|---|
| Refrigerator | 100-200 |
| Freezer | 75-150 |
| Dishwasher | 1200-1800 |
| Washing Machine | 500-1500 |
| Clothes Dryer | 2000-5000 |
| Oven (Electric) | 2500-5000 |
| Microwave Oven | 700-1200 |
| Coffee Maker | 750-1500 |
| Television (LCD) | 50-200 |
| Computer (Desktop) | 100-300 |
| Laptop | 30-100 |
| Incandescent Light Bulb | 40-100 |
As you can see, appliances like clothes dryers, ovens, and dishwashers consume significantly more power than others, such as refrigerators and televisions. This information can guide you in making informed choices about when and how to use these appliances to minimize energy consumption and reduce your electricity bill.
Beyond Wattage: Unveiling the 'Hidden' Energy Consumption
The power consumption chart above provides a valuable snapshot of appliance energy use. However, it's important to recognize that some appliances consume energy even when they're not actively in use. This 'hidden' energy consumption, known as standby power, can add up over time, contributing to a higher energy bill.
Standby Power: The Silent Energy Drain
Many electronic devices, like televisions, computers, and phone chargers, continue to draw a small amount of power even when turned off. This phenomenon, known as standby power, is often overlooked but can significantly impact your energy consumption. Appliances in standby mode may consume anywhere from a few watts to several tens of watts, depending on the device.
To illustrate the impact of standby power, consider a television that consumes 10 watts in standby mode. If left on standby for 24 hours a day, it would consume 0.24 kilowatt-hours (kWh) of energy per day. Over a year, this translates to 87.6 kWh, which could add a significant sum to your electricity bill. While the individual consumption of each device might seem insignificant, the combined effect of multiple appliances in standby mode can be substantial.
Confronting the Energy Challenge: Tips for Reducing Appliance Power Consumption
Now that we've explored the power consumption of different appliances, let's delve into practical tips for reducing your energy use and saving money.
Simple Steps for Minimizing Energy Waste
Here are some simple yet effective strategies to reduce your appliance energy consumption:
- Unplug appliances when not in use: This simple act can significantly reduce standby power consumption. Unplug chargers, televisions, and other devices when not in use, even if they're turned off.
- Use power strips: Power strips with on/off switches allow you to easily turn off multiple appliances at once, eliminating standby power consumption. This is particularly useful for electronics like TVs, computers, and gaming consoles.
- Choose energy-efficient appliances: When purchasing new appliances, look for the Energy Star label, which indicates that the appliance meets specific energy-efficiency standards.
- Optimize appliance settings: Utilize power-saving features on your appliances, such as the "eco" mode on washing machines or the "sleep" mode on televisions. Adjust the temperature settings on your refrigerator and freezer to maintain optimal cooling without excessive energy consumption.
- Reduce appliance usage: Consider alternative methods for tasks, such as air drying clothes instead of using a dryer or using a microwave instead of an oven for smaller meals.
- Maintain appliances regularly: Clean filters and coils on your refrigerator and dryer to ensure optimal performance and reduce energy consumption. A well-maintained appliance functions more efficiently and consumes less energy.
By implementing these simple tips, you can significantly reduce your energy consumption and make a positive impact on your environment and your wallet.
The Power of Knowledge: Making Informed Choices
Understanding the power consumption of your appliances is the first step towards making informed choices about your energy usage. By educating yourself about the energy demands of your household, you can take control of your energy consumption, minimize your electricity bill, and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Frequently Asked Questions About Appliance Power Consumption Charts
What is an appliance power consumption chart?
An appliance power consumption chart lists common household appliances and their typical wattage ratings. This chart helps you understand how much energy each appliance uses.
Why is it important to understand appliance power consumption?
Knowing your appliances' power consumption helps you make informed decisions about energy usage, potentially reducing your electricity bill and environmental impact.
How can I use a power consumption chart to save energy?
- Switch off appliances when not in use: This simple act can significantly reduce your energy bill.
- Prioritize energy-efficient appliances: When purchasing new appliances, consider their energy rating and choose models that consume less power.
- Utilize power-saving features: Many modern appliances come with built-in energy-saving features. Take advantage of these options to further reduce your energy consumption.
- Use appliances strategically: For example, consider using a microwave instead of an oven for smaller meals, as microwaves generally consume less energy.
Where can I find a power consumption chart for appliances?
You can find appliance power consumption charts online, in energy-saving guides, or on the websites of utility companies. You can also check the energy label on appliances for their wattage ratings.
What factors affect the power consumption of an appliance?
Factors that can influence an appliance's power consumption include:
- Size: Larger appliances generally consume more power.
- Age: Older appliances tend to be less energy-efficient than newer models.
- Efficiency: Appliances with higher energy efficiency ratings consume less power.
- Usage frequency: The more you use an appliance, the more energy it consumes.
- Settings and cycles: Different settings and cycles on appliances can impact their power consumption.