Harnessing the Power of Nature: The Top 3 Ways Electricity is Produced

Electricity, a force that powers our modern world, is generated through various methods, each with its own advantages and drawbacks. But how exactly is this invisible force created? Let's delve into the three primary ways electricity is produced, highlighting their key features and environmental impacts.
1. Thermoelectric Power: The Heat of Combustion
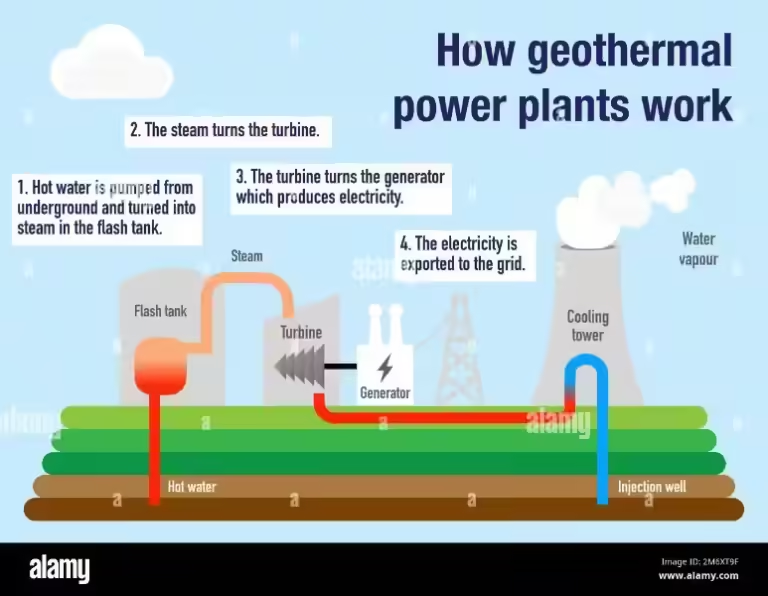
Thermoelectric power plants, the most common method of electricity generation worldwide, utilize the burning of fossil fuels like coal, natural gas, and oil to create heat. This heat is then used to convert water into high-pressure steam, which drives turbines connected to generators, ultimately producing electricity.
Think of it like this: Imagine a giant kettle where fossil fuels act as the fire, heating the water. The steam produced from the boiling water then spins a turbine, much like the spinning of a wheel, and this spinning motion generates electricity.
While thermoelectric power offers efficiency and readily available fuel sources, it comes with significant environmental drawbacks. The burning of fossil fuels releases harmful greenhouse gases, primarily carbon dioxide, which contribute to climate change and air pollution. This has led to widespread concern about the long-term sustainability of this method, prompting the development of cleaner alternatives.
2. Wind Power: Capturing the Breeze
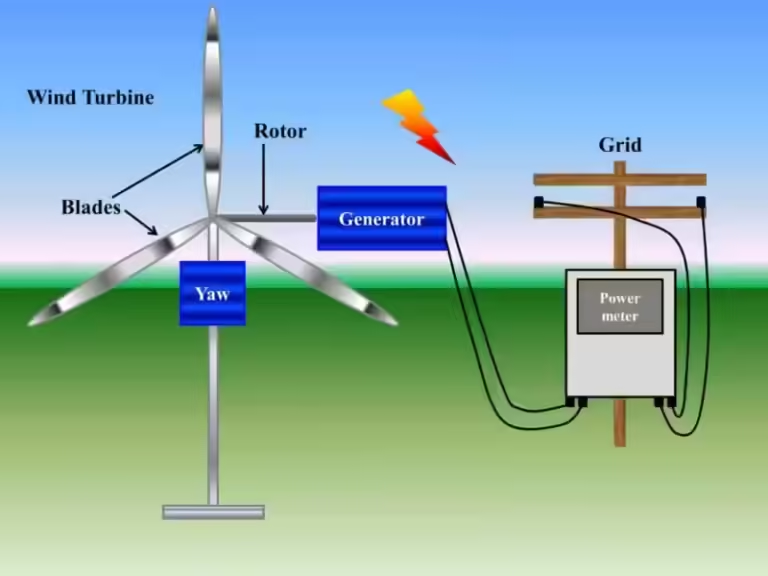
Wind turbines, those towering structures that dot landscapes around the world, utilize the kinetic energy of wind to generate electricity. Their blades, designed like airplane wings, spin when exposed to wind, driving a generator connected to a shaft. This spinning motion creates electricity, much like a bicycle dynamo generates power when you pedal.
Wind power stands out as a renewable and clean energy source, significantly reducing greenhouse gas emissions and waste. However, its widespread adoption faces challenges. Firstly, the initial cost of building and installing wind turbines can be high. Secondly, the location of wind turbines must be carefully considered to ensure sufficient wind resources, often limiting their placement.
3. Solar Power: Harnessing the Sun’s Energy
Solar energy, as the name suggests, harnesses the sun's energy to generate electricity. The most common method involves photovoltaic panels, which convert sunlight directly into electricity. These panels are composed of semiconductor materials that absorb sunlight and release electrons, creating an electrical current. The stronger the sunlight, the more electricity is generated.
Think of it like this: Imagine a solar panel as a giant battery that continuously charges itself whenever exposed to sunlight. The more sunlight it receives, the more power it generates.
Solar energy stands as a clean, sustainable alternative to fossil fuels, but it comes with its own limitations. Its dependence on sunlight restricts its effectiveness in regions with limited sunshine or during nighttime hours. Additionally, the initial cost of solar panel installation can be high, although prices are steadily decreasing.
Each of these electricity generation methods plays a crucial role in powering our world, but each presents its own set of challenges and opportunities. While thermoelectric power remains the dominant source due to its efficiency and readily available fuel, its environmental impact drives the search for cleaner alternatives. Wind and solar power offer promising solutions, but their cost and limitations in certain regions necessitate ongoing research and development. Ultimately, the future of electricity generation depends on finding a balance between efficiency, sustainability, and accessibility to create a clean and reliable energy future for all.