The Energetic World of Light: A Journey Through Wavelength and Frequency

Imagine a world where colors dance with energy, and the vibrancy of hues holds the key to understanding the universe. That's the world of light, a fascinating entity that not only illuminates our surroundings but also reveals the secrets of the cosmos. Light, in its simplest form, is a form of electromagnetic radiation. It travels in waves, just like ripples on a pond, and these waves carry energy. The more energy a wave of light carries, the more intense it is. This intensity is directly linked to the wave's frequency and wavelength.
Think of it this way: a wave with a higher frequency is like a swimmer taking more strokes per minute, while a wave with a lower frequency is like a swimmer taking fewer strokes per minute. The higher the frequency, the more energy the wave carries, and the shorter its wavelength. This relationship between frequency, wavelength, and energy is fundamental to understanding light's behavior and its interactions with the world around us.
The Spectrum of Light: A Rainbow of Energy
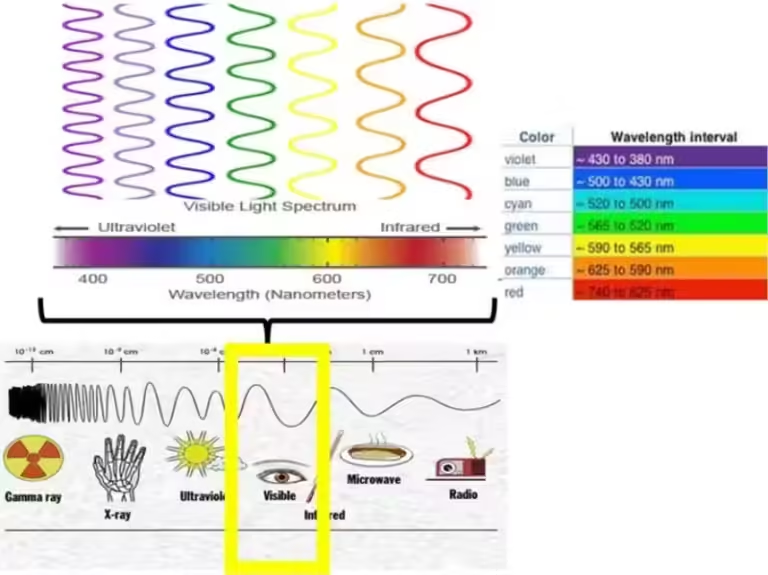
We experience light as a spectrum of colors, from the deep red of a setting sun to the vibrant blue of a clear sky. Each color in this spectrum represents light with a different wavelength and frequency, hence a different energy level. Red light, for instance, has a longer wavelength and lower frequency, indicating lower energy. Conversely, violet light has a shorter wavelength and higher frequency, indicating higher energy.
This spectrum of colors is not only a beautiful visual phenomenon but also a powerful tool for scientists. By studying the light emitted or absorbed by objects, astronomers can determine their composition, temperature, and even their motion. Think of it as a cosmic fingerprint, revealing the secrets of distant stars and galaxies.
Visible Light: The Spectrum We See
The visible light spectrum is the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that our eyes can detect. This narrow band of wavelengths, ranging from about 400 nanometers (violet) to 700 nanometers (red), is responsible for the vibrant colors we see in our daily lives. But beyond this visible range lie other forms of light, invisible to our eyes but equally important in understanding the universe.
Imagine a vast ocean of electromagnetic radiation, with visible light being just a small ripple on its surface. Beyond the visible spectrum, we have the infrared and ultraviolet regions, each carrying different amounts of energy and playing crucial roles in various scientific applications.
Beyond Visible Light: Unveiling the Invisible
While visible light illuminates our world, other forms of electromagnetic radiation, invisible to our eyes, hold the key to understanding phenomena beyond our immediate perception. These invisible forms of light, each with its unique energy signature, reveal a hidden universe of energy and information.
Infrared Radiation: The Heat We Feel
Infrared radiation, with wavelengths longer than visible light, carries less energy. It is the warmth we feel from the sun or a hot stove. Astronomers use infrared telescopes to study cold, dusty regions of space, where stars are born, and to detect the heat signatures of distant planets.
Think of infrared radiation as a thermal map of the universe, revealing hidden heat sources and revealing the secrets of celestial objects.
Ultraviolet Radiation: The Energy of the Sun
Ultraviolet radiation, with wavelengths shorter than visible light, carries more energy. This high-energy radiation is responsible for sunburns and can damage our DNA. However, it also plays a crucial role in life on Earth, driving the process of photosynthesis in plants. Astronomers use ultraviolet telescopes to study hot, energetic objects like quasars and supernovae.
Imagine ultraviolet radiation as a cosmic spotlight, illuminating the most energetic and violent events in the universe, providing insights into the evolution of stars and galaxies.
The Significance of Light’s Energy: From Technology to the Cosmos
Light's energy is not just a scientific curiosity; it is a driving force behind many technologies and natural phenomena. From the lasers used in surgery and telecommunications to the solar panels that power our homes, light's energy is shaping our world in profound ways.
The energy of light also drives the processes that create and sustain life on Earth. Photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy, is a testament to the power of light's energy. Without light's energy, life as we know it would not exist.
The Future of Light: Exploring the Unknown
As we delve deeper into the mysteries of the universe, the study of light's energy continues to reveal new wonders. Scientists are exploring ways to harness the power of light for energy production, medical treatments, and even space travel.
From understanding the fundamental nature of light to exploring its potential for shaping our future, the energy of light remains a captivating and essential part of our understanding of the universe.
Frequently Asked Questions
If light has a lot of energy, what will it have?
High frequency and short wavelength.