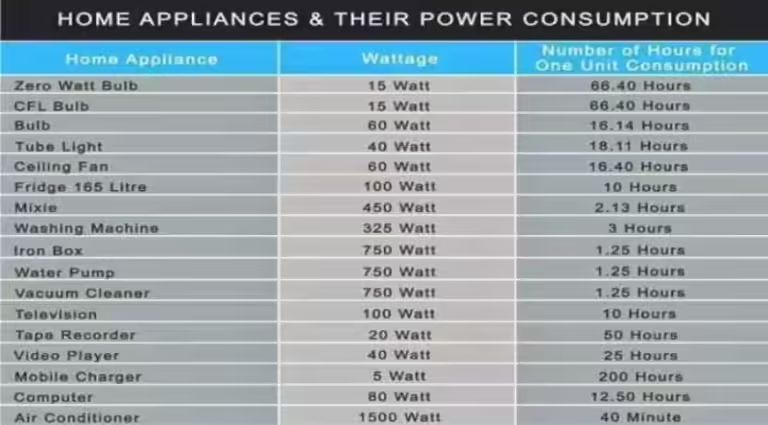
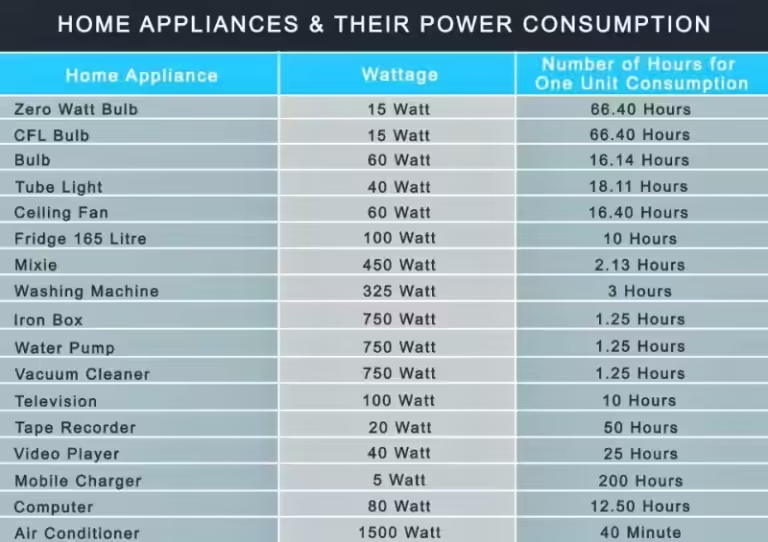
How Much Electricity Does the Average UK House Use?
Understanding your household's electricity consumption is crucial for making informed decisions about your energy usage and reducing your environmental impact. This article provides a comprehensive overview of average electricity usage in UK homes, exploring key factors influencing consumption and offering practical tips for saving energy.
Average Electricity Consumption in UK Homes
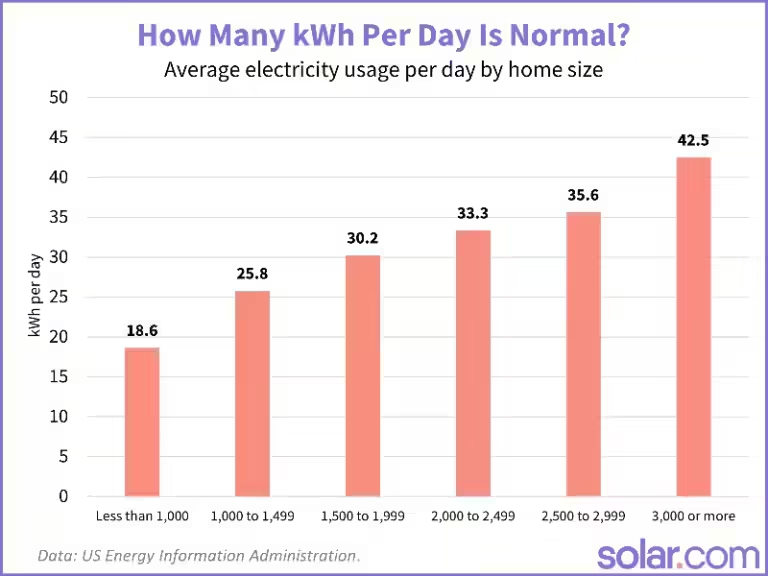
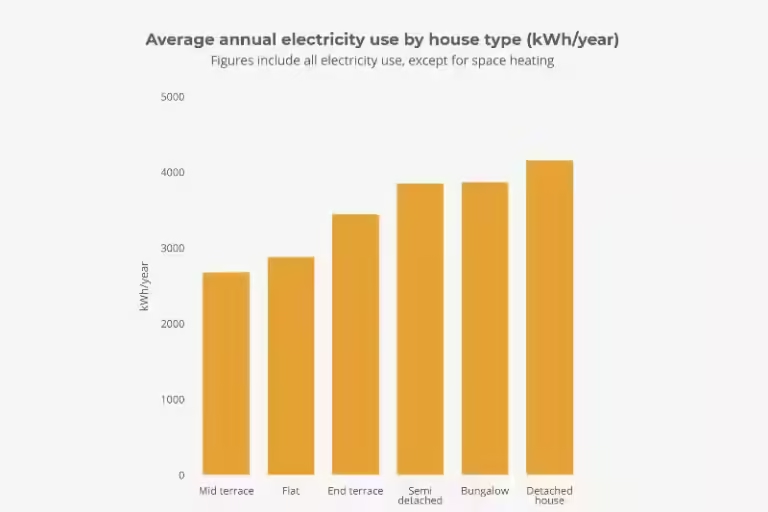
The average UK household consumes approximately 2,900 kWh (kilowatt-hours) of electricity per year. This figure, however, is just a starting point, as actual consumption varies significantly depending on several factors, including:
-
Home Size: Larger homes generally consume more electricity due to increased space for heating, lighting, and appliance usage. For instance, a detached house might use significantly more electricity than a small flat.
-
Number of Occupants: The more people living in a house, the more appliances are likely to be in use. A family of four will naturally consume more electricity than a single person living alone.
-
Energy Efficiency: Well-insulated homes with efficient appliances and lighting systems consume less energy than older, poorly insulated homes with outdated appliances.
Breaking Down Electricity Usage: Where Does It Go?
While the average household electricity consumption serves as a general guideline, understanding where that electricity goes is crucial for identifying areas for potential savings. Here's a breakdown of typical electricity usage in a UK home:
1. Wet Appliances: The Biggest Consumers
Washing machines, dishwashers, and tumble dryers are among the most energy-intensive appliances in a home, collectively accounting for approximately 14% of total electricity consumption. Using these appliances efficiently can significantly impact your energy bill.
-
Washing Full Loads: Washing clothes with full loads instead of half-full ones can save considerable energy. Aim for a full drum to minimize the number of cycles needed.
-
Cold Wash Cycles: Utilize cold water wash cycles whenever possible, as heating water for washing consumes a large amount of energy.
-
Air Drying: Instead of using a tumble dryer, try air-drying your clothes whenever possible. This can save you significant energy and money.
2. Cold Appliances: Keeping Food Fresh
Refrigerators and freezers are also major electricity consumers, accounting for another 13% of total consumption. Maintaining these appliances properly can reduce their energy usage:
-
Regular Defrosting: Defrost your freezer regularly to prevent the build-up of ice, which can hinder efficient cooling and increase energy usage.
-
Correct Temperature Settings: Ensure your fridge and freezer are set to the correct temperature for optimal efficiency.
-
Keep Them Full: A full refrigerator or freezer maintains a consistent temperature, minimizing energy consumption.
3. Electronic Devices: The Silent Drain
Televisions, laptops, computers, and game consoles might not seem like major electricity consumers, but they collectively contribute to 6% of total household electricity use.
-
Turning Off Devices Completely: Even when devices are on standby mode, they still consume a small amount of electricity. Turn off devices fully when not in use.
-
Energy-Saving Modes: Utilize energy-saving modes on devices like televisions to reduce their power consumption.
4. Lighting: Making the Switch
Lighting accounts for 5% of total electricity consumption. Replacing traditional incandescent bulbs with energy-efficient LED bulbs can significantly reduce energy usage and lower your electricity bill.
-
LED Bulbs: LED bulbs use significantly less energy than traditional incandescent bulbs and last much longer.
-
Motion Sensors: Install motion sensors in areas like hallways and bathrooms to automatically turn lights off when not in use.
-
Natural Light: Make the most of natural daylight by keeping blinds and curtains open during the day to reduce reliance on artificial lighting.
5. Cooking: Efficient Heating
Cooking appliances such as hobs, ovens, kettles, and microwaves consume 4% of total electricity. Using these appliances efficiently can make a difference:
-
Use the Right Size Pot: Choose pots and pans that are appropriate for the size of the burner to avoid wasting heat.
-
Microwave Cooking: Microwave cooking is often more energy-efficient than using conventional ovens.
-
Cover Pots: Covering pots while cooking helps retain heat and reduces cooking time.
Tips for Reducing Your Household Electricity Consumption
Reducing your home's electricity consumption not only benefits your wallet but also helps the environment. Here are some practical tips to implement:
-
Thermostat Adjustment: Lowering your thermostat by just 1°C can save up to 10% on heating costs.
-
Radiator Optimization: Ensure your radiators are not blocked by furniture or curtains and bleed them regularly to ensure efficient heat distribution.
-
Smart Meters: Smart meters provide real-time information on your energy usage, enabling you to make informed decisions about your energy consumption.
-
Energy-Saving Plugs: Use energy-saving plugs to cut standby power consumption by completely powering off appliances when not in use.
-
Home Insulation: Improve your home's insulation to reduce heat loss and keep your home warm in the winter without relying on excessive heating.
-
Solar Panels: Installing solar panels can significantly reduce your reliance on the grid and save money on your electricity bill.
Understanding Your Energy Bill
Your electricity bill provides valuable information about your energy usage patterns and costs. Here's a breakdown of key components:
-
Standing Charge: This fixed charge covers the cost of maintaining the electricity network.
-
Unit Charge: This charge reflects the cost of the electricity you use, measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh).
-
VAT: Value-added tax is applied to your total energy bill.
-
Average Consumption: Your energy bill often includes information on your average electricity consumption, allowing you to track your usage over time and identify potential savings opportunities.
Summary: Making Informed Choices About Your Electricity Usage
By understanding your household's electricity consumption patterns, identifying areas for potential savings, and implementing practical tips, you can reduce your energy bill, lower your environmental impact, and make informed choices about your energy usage.
Frequently Asked Questions
How much electricity does the average UK home use?
The average UK household uses approximately 2,900 kWh of electricity per year.
What factors affect how much electricity a UK home uses?
Factors affecting electricity usage include home size, number of occupants, energy efficiency, and appliance usage.
How much electricity does a UK home use per day?
The average daily electricity usage can vary from 4.93 kWh/day (low) to 11.78 kWh/day (high).
What appliances use the most electricity in a UK home?
Washing machines, tumble dryers, dishwashers, refrigerators, freezers, and electronics are among the most energy-intensive appliances.
How can I reduce my electricity usage in my UK home?
Reduce your electricity usage by lowering the thermostat, optimizing radiators, using smart meters, employing energy-saving plugs, and improving home insulation.