How Many Kilowatt Hours Does an Apartment Use?
Navigating the world of electricity bills can be daunting, especially for apartment dwellers. Knowing how many kilowatt-hours (kWh) your apartment uses can help you budget, understand your energy consumption, and potentially save money. But the question of "How many kWh does an apartment use?" isn't a simple one. There are many factors at play, and understanding them is crucial to making informed decisions about your energy usage.
Average Apartment Energy Consumption: A Starting Point
While every apartment is unique, a general idea of average usage can provide a starting point for understanding your electricity bill. A typical one-bedroom apartment (around 750 square feet) might use approximately 750 kWh per month. Larger apartments, such as those with two bedrooms and 1,000 square feet, often use around 880 kWh per month. This increased usage can be attributed to the need for more heating and cooling in a larger space.
Factors Influencing Apartment Energy Usage
Here's a detailed breakdown of the factors that contribute to how much electricity your apartment uses:
1. Apartment Size and Layout
Larger apartments naturally require more energy to heat, cool, and power. A two-bedroom apartment with high ceilings will typically use more electricity than a cozy studio with minimal space. The layout of the apartment also plays a role. A south-facing apartment, for example, might receive more sunlight and require less artificial lighting.
2. Age and Energy Efficiency
Older apartments may have less efficient insulation and outdated appliances, leading to higher energy consumption. Newer apartments often feature modern appliances and improved insulation, which can significantly reduce electricity usage.
3. Number of Residents and Lifestyle
More residents mean more energy use. A family of four will likely consume more electricity than a single person, especially if they have young children who use lights and electronics frequently. Individual habits, such as taking long showers or leaving lights on in empty rooms, also significantly impact energy consumption.
4. Appliances and Electronics
The number and type of appliances you use heavily influence energy consumption. A kitchen with a dishwasher, microwave, and electric stove will consume more electricity than a kitchen with just a refrigerator and a gas stove. Electronic devices like televisions, computers, and charging devices also add to your energy bill.
5. Heating and Cooling Systems
Heating and cooling systems are major consumers of electricity. A large air conditioner or heating system will use more energy than a smaller one. The efficiency of these systems also plays a role. An older, inefficient unit will require more energy to reach the desired temperature.
6. Window Quality and Insulation
Drafty windows and poor insulation can lead to significant heat loss in the winter and heat gain in the summer, forcing your heating and cooling systems to work harder. This translates into higher energy consumption and higher electricity bills. Double-paned windows and proper insulation can significantly improve energy efficiency.
Beyond the Average: Personalizing Your Energy Usage
While averages provide a starting point, understanding your specific circumstances is key to accurately estimating your apartment's energy usage. Consider the following:
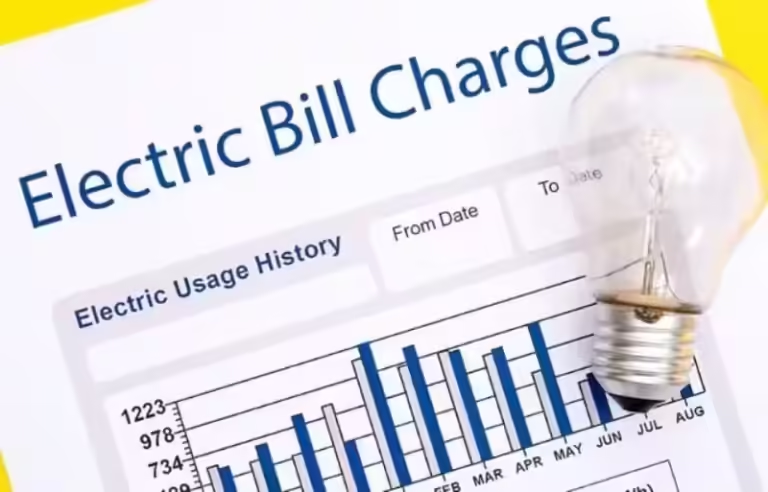
- Past Performance: Use your previous electricity bills as a baseline. If you've lived in a similar-sized apartment before, your old bills can give you a good starting point for comparison.
- Asking Around: Talk to previous tenants or neighbors about their electricity bills. They might be able to share insights into the average usage for your specific building.
- Key Differences: Compare your new apartment to your old one. Is it larger? Does it have a different air conditioning unit? Are there more appliances? Are the windows older or newer? These factors can impact your energy consumption.
Taking Control: Energy-Saving Tips for Apartment Dwellers
Even if you can't change the size of your apartment or the age of your appliances, you can still make a difference in your energy consumption. Here are some practical tips:
- Use Energy-Efficient Appliances and Light Bulbs: Look for Energy Star-rated appliances and LED light bulbs, which consume less energy and can save you money in the long run.
- Turn Off Lights When Leaving Rooms: This simple habit can make a significant difference in your overall energy consumption.
- Utilize Natural Light: Open blinds and curtains during the day to take advantage of natural light and reduce your reliance on artificial lighting.
- Adjust Thermostat Settings: Set your thermostat to a comfortable temperature and avoid extreme settings. A few degrees can make a difference in your energy usage.
- Insulate Windows and Doors: Use weatherstripping or draft excluders to prevent heat loss and improve energy efficiency.
- Use Fans to Circulate Air: Circulating air can help cool your apartment without relying solely on air conditioning.
- Unplug Electronic Devices When Not in Use: Even when turned off, devices plugged into an outlet continue to draw a small amount of power. Unplugging them when not in use can save energy.
- Consider a Smart Meter: Smart meters provide real-time feedback on your energy usage, helping you understand your consumption patterns and identify areas for improvement.
Understanding Your Energy Consumption Is Key
By understanding the factors that influence your apartment's energy consumption and implementing energy-saving strategies, you can not only reduce your electricity bill but also make a positive impact on the environment. Remember, every small step towards energy efficiency adds up!
Frequently Asked Questions About Apartment Electricity Usage
How much electricity does a typical apartment use?
A one-bedroom apartment around 750 square feet uses roughly 750 kWh per month, while a larger one around 1000 square feet uses around 880 kWh.
What factors affect how much electricity an apartment uses?
The size of the apartment, its age, and energy efficiency all play a role. A larger apartment, an older building, and poor insulation will lead to higher energy consumption.
How can I estimate my electricity usage for a new apartment?
Look at your past electricity bills and consider the differences between your old and new apartments, like size, appliance count, and window quality. You can also ask previous tenants about their bills.
Do apartments use less electricity than houses?
Yes, apartments generally use less electricity than houses because they share walls, which reduces heating and cooling loss.
What are some tips for reducing my apartment's electricity usage?
Use energy-efficient appliances and light bulbs, turn off lights when leaving rooms, utilize natural light whenever possible, adjust your thermostat settings, and unplug electronics when not in use.