The Great EV Charging Time Debate: Why Some EVs Take Longer to Charge
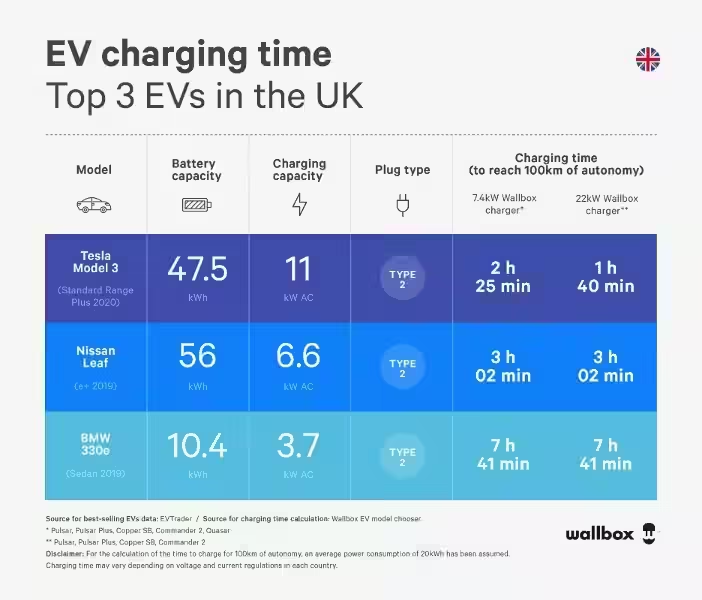
The transition to electric vehicles (EVs) is gaining momentum, but one persistent question remains: how long does it take to charge an EV? The answer, unfortunately, isn't simple. While some EVs can charge quickly, others, especially those with larger batteries, take the longest time to charge from empty. Factors like battery size, charging method, and charger speed all play a role in determining how long you'll be tethered to the charging station.
Battery Size: The Bigger They Are, The Longer They Take
The first culprit behind long charging times is often the battery itself. EVs with larger batteries, which provide longer driving ranges, naturally take longer to charge. Think of it like filling a bathtub - a bigger tub requires more water to fill. Similarly, a larger battery requires more energy to reach a full charge. This is why some EVs will take the longest time to charge from empty, especially those designed for long-distance driving.
For example, a compact electric car with a 30 kWh battery might charge fully in a few hours using a Level 2 charger, while a large SUV with an 80 kWh battery could take twice as long. Even within the same model, a higher trim level with a larger battery will typically have a longer charging time.
Charging Methods: From Slow to Fast
The charging method you use also significantly impacts the charging time. EVs can be charged using three primary methods:
Level 1 Charging: The Slowest Option
Level 1 charging uses a standard 120-volt household outlet, the same one you use for appliances like lamps and toasters. This method is the slowest option, taking 5+ hours for plug-in hybrids (PHEVs) and a whopping 30-50+ hours for full EVs to fully charge. Level 1 charging is suitable for overnight charging at home or as a backup when other options are unavailable.
Level 2 Charging: The Everyday Hero
Level 2 charging utilizes a 240-volt outlet, often found in garages or dedicated charging stations. It's much faster than Level 1, typically taking 1-2 hours for PHEVs and 4-10 hours for full EVs to charge. Level 2 charging is the most popular and convenient option for everyday use, and many homeowners install Level 2 chargers for their EVs.
DC Fast Charging: The Road Trip Savior
DC fast charging, also known as DCFC or fast charging, is the fastest way to charge an EV. It utilizes high-voltage direct current (DC) electricity, delivering power much faster than Level 1 or Level 2. DC fast chargers are commonly found at public charging stations and can charge full EVs to 80% in 20 minutes to 1 hour. However, most PHEVs aren't compatible with DC fast charging, so they still rely on Level 1 or Level 2 options.
Charger Speed: A Game of Watts
Even within DC fast charging, speeds vary based on the charger's wattage. Higher wattage means faster charging, with chargers ranging from 15 kW to 350+ kW. However, the maximum charging rate of your EV also plays a role. Even if a charger offers 350 kW, your EV might only be able to accept 150 kW, limiting the charging speed. This means that some EVs will take the longest time to charge from empty even at a fast-charging station, simply because their battery and charging system can't handle the full power output.
Beyond the Basics: Other Factors Influencing Charging Time
Beyond battery size and charging method, several other factors can affect how long it takes to charge an EV:
- Battery Charge Level: Charging from a lower percentage takes longer than charging from a higher percentage. For example, charging from 20% to 80% will be faster than charging from 10% to 100%.
- Charging Beyond 80%: Once an EV reaches around 80% charge, the charging speed significantly slows down to protect the battery's lifespan. This is why it's generally recommended to limit fast charges to 80% for optimal battery health.
- Weather: Colder temperatures can negatively impact charging speed, as the battery needs more energy to warm up before accepting a charge. Conversely, warmer temperatures can slightly improve charging efficiency.
Key Takeaways: Navigating the Charging Landscape
The length of time it takes to charge an EV is a complex issue with no simple answer. However, understanding the factors involved can help you make informed decisions about your EV choices and charging habits. Here are some key takeaways:
- PHEVs generally charge much faster than full EVs, especially using Level 1 or Level 2 charging.
- Level 2 home charging is the most convenient option for everyday use, providing a reasonable charging time for the majority of EVs.
- DC fast charging is ideal for long trips but should be limited to 80% for optimal battery life and to avoid extended charging times.
- Charging time varies significantly based on a combination of factors, so it's essential to consider these when choosing an EV and charging method.
Ultimately, the best way to determine the charging time for a specific EV is to consult the manufacturer's website or user manual. But armed with this knowledge, you can confidently navigate the world of EV charging and embrace the exciting future of electric mobility.
Frequently Asked Questions About EV Charging Times
Which EVs take the longest to charge?
Generally, EVs with larger battery capacities take the longest to charge. While this provides a greater driving range, it also means more energy needs to be transferred, potentially lengthening charging times.








