Energy Storage: The Backbone of a Sustainable Future

In a world increasingly reliant on electricity, the ability to store energy is becoming paramount. Energy storage is the primary function of technologies that allow us to capture and hold energy for later use. This capability is crucial for addressing the inherent variability of renewable energy sources, ensuring grid stability, and enabling a more sustainable future.
Imagine a world powered entirely by the sun. The sun shines brightly during the day, but what happens when the sun sets? Without energy storage, we would be left in the dark. This highlights the critical role of energy storage in bridging the gap between energy supply and demand.
Types of Energy Storage
Energy storage solutions come in various forms, each with its unique strengths and applications.
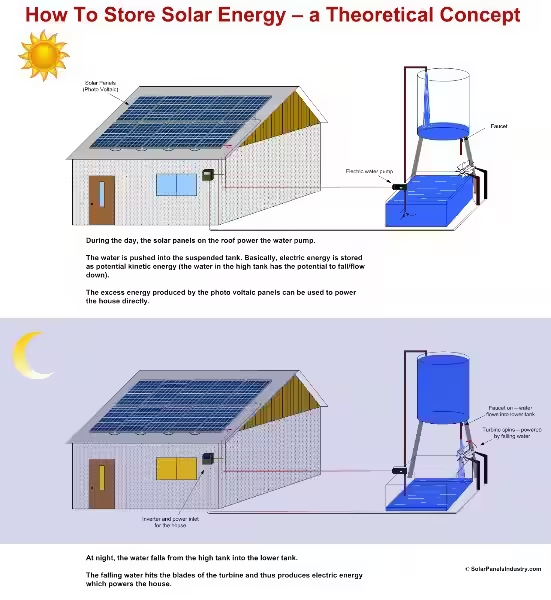
1. Pumped Hydroelectric Storage (PHS)
Energy storage is the primary function of pumped hydroelectric storage (PHS), the oldest and most mature energy storage technology. PHS utilizes excess electricity to pump water uphill to a reservoir. When demand exceeds generation, water flows back downhill through turbines, generating electricity. PHS is highly efficient, but its geographical limitations restrict its widespread adoption.
2. Batteries
Energy storage is the primary function of batteries, which are rapidly gaining prominence in the energy storage landscape. Batteries store energy chemically, allowing for the release of electricity when needed. Lithium-ion batteries, known for their high energy density, are widely used in electric vehicles, portable electronics, and grid-scale storage applications.
3. Compressed Air Energy Storage (CAES)
Energy storage is the primary function of compressed air energy storage (CAES), a technology that stores energy by compressing air into underground caverns or tanks. When energy is needed, the compressed air is released to drive turbines, generating electricity. CAES offers long-duration storage and can be integrated with renewable energy sources.
4. Thermal Energy Storage
Energy storage is the primary function of thermal energy storage, which utilizes the heat or cold of a substance to store energy. For example, molten salt can store heat from solar thermal power plants, releasing it later to generate electricity.
Benefits of Energy Storage
Energy storage offers numerous benefits, making it an essential component of a sustainable energy future.
1. Grid Stability
Energy storage is the primary function of stabilizing the grid by providing backup power during peak demand or outages. It also helps to buffer the intermittency of renewable energy sources, ensuring a consistent and reliable energy supply.
2. Renewable Energy Integration
Energy storage is the primary function of enabling the seamless integration of renewable energy sources like solar and wind power. By storing excess energy generated during peak production times, energy storage allows for the utilization of renewable energy when it's not available.
3. Reduced Emissions
Energy storage is the primary function of reducing greenhouse gas emissions by providing a clean and efficient way to store and manage energy. This promotes the transition towards a low-carbon economy.
Challenges and Future of Energy Storage
While energy storage holds immense potential, it faces certain challenges that need to be addressed.
1. Cost
Energy storage is the primary function of a technology that is still in its early stages of development, and costs can be prohibitively high for some applications. Continued research and advancements in battery technology are crucial for reducing costs and making energy storage more accessible.
2. Durability and Lifespan
Energy storage is the primary function of a technology that needs to be reliable and durable. Batteries, for instance, have a limited lifespan and degrade over time. Research and development are ongoing to enhance the durability and lifespan of energy storage systems.
3. Safety
Energy storage is the primary function of a technology that needs to be safe. Incidents involving battery fires have raised concerns about the safety of energy storage. Implementing stringent safety standards and developing more robust battery designs are essential for ensuring the safe operation of energy storage systems.
Despite these challenges, the future of energy storage is bright. Continued research, technological advancements, and government support are driving the development of more efficient, affordable, and sustainable energy storage solutions. These innovations will play a crucial role in unlocking the full potential of renewable energy and shaping a more sustainable future.
Frequently Asked Questions about Energy Storage
What is the primary function of energy storage?
Energy storage is the process of capturing and holding energy for later use.
Why is energy storage important?
Energy storage is crucial for:
- Balancing supply and demand: Storing energy during periods of low demand and releasing it during peak demand.
- Improving grid reliability: Ensuring a consistent supply of energy even when renewable sources like solar and wind are intermittent.
- Reducing reliance on fossil fuels: Enabling the transition to cleaner and sustainable energy sources.
What are some examples of energy storage technologies?
Common energy storage technologies include:
- Batteries: Electrochemical devices that store energy in chemical form.
- Pumped hydro: Using excess energy to pump water uphill, releasing it for power generation later.
- Compressed air energy storage (CAES): Storing energy by compressing air, then releasing it to drive a turbine.