Decoding Your Electrical Appliance Power Consumption: A Guide to Energy Efficiency
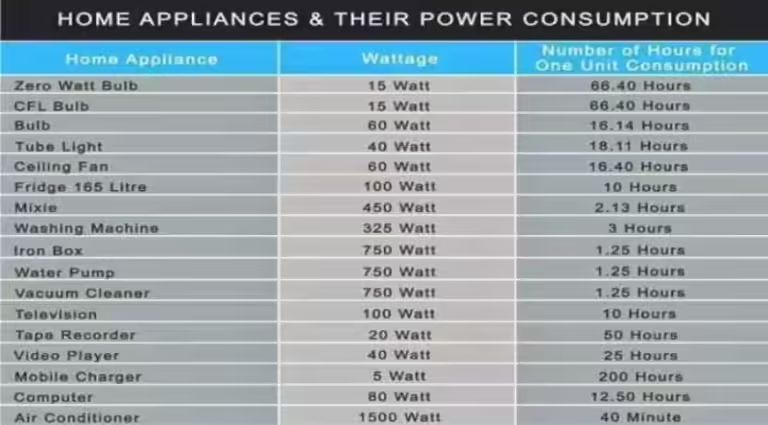
Have you ever wondered how much energy your refrigerator consumes compared to your TV? Do you know which appliances are the biggest energy guzzlers in your home? Understanding the power consumption of your electrical appliances is crucial for making informed decisions about your energy usage and potentially saving money on your electricity bill. This comprehensive guide will provide you with a clear understanding of the power consumption of various appliances, equipping you with the knowledge to manage your energy consumption effectively.
The Power Consumption Chart: Your Energy Usage Guide
The table below presents a comprehensive overview of the typical power consumption values for common household appliances, measured in Watts. This data serves as a valuable starting point for assessing your energy usage and identifying areas for potential improvement.
| Appliance | Typical Power Consumption (Watts) |
|---|---|
| Refrigerator | 150-250 |
| Freezer | 100-200 |
| Dishwasher | 1,200-1,800 |
| Washing Machine | 500-1,500 |
| Clothes Dryer | 3,000-4,000 |
| Oven | 2,500-3,500 |
| Microwave Oven | 700-1,200 |
| Coffee Maker | 800-1,200 |
| Television | 50-300 |
| Computer | 100-300 |
| Hair Dryer | 1,500-2,000 |
| Iron | 1,000-1,500 |
| Vacuum Cleaner | 600-1,200 |
| Ceiling Fan | 75-150 |
It's important to note that these figures are estimations, and actual power consumption can vary depending on the appliance's model, age, and usage patterns. For precise measurements, consider using a clamp-on ammeter or a Kill-A-Watt meter to measure the amperage draw directly from the appliance.
Understanding the Impact of Power Consumption
Power consumption is measured in Watts (W) and represents the rate at which an appliance uses energy. The higher the wattage, the more energy the appliance consumes. To determine the total energy used by an appliance, we need to consider its wattage and the duration of its usage. We can calculate the daily energy consumption in watt-hours (Wh) using the following formula:
Daily Energy Consumption (Wh) = Wattage (W) x Hours of Usage (h)
For instance, a refrigerator with a wattage of 150W running for 24 hours a day consumes 3,600 Wh (150W x 24h). This information helps you understand the energy consumption of different appliances and identify potential areas for saving energy.
Tips to Reduce Appliance Power Consumption
Now that you have a clear understanding of power consumption, let's explore some practical tips to reduce your energy usage and save money on your electricity bill:
1. Optimize Appliance Usage
Reduce the time you spend using high-power appliances like ovens, hairdryers, and vacuum cleaners. Opt for shorter laundry cycles and air-dry your clothes whenever possible. Consider using a pressure cooker for cooking instead of your oven for faster and more energy-efficient cooking.
2. Upgrade to Energy-Efficient Models
Newer appliances often feature energy-saving technologies that can significantly reduce their power consumption. Look for appliances with the Energy Star label, which indicates that they meet specific energy efficiency standards. Upgrading to energy-efficient models can result in long-term cost savings and a reduced environmental impact.
3. Unplug Unused Devices
Many devices, like TVs, computers, and phone chargers, continue to consume energy even when switched off. Unplugging them when not in use can help reduce your energy consumption and save money. Consider using power strips with on/off switches to easily turn off multiple devices simultaneously.
4. Invest in Energy-Saving Measures
Consider implementing energy-saving measures like installing LED light bulbs, using smart thermostats, and sealing air leaks in your home. These measures can significantly reduce your overall energy consumption and contribute to a more sustainable lifestyle.
Conclusion: Empowering Your Energy Decisions
By understanding the power consumption of your appliances and implementing energy-saving practices, you can take control of your energy usage and reduce your electricity bill. Remember to consider the wattage, usage duration, and potential upgrades when making decisions about your appliances. With this knowledge, you can make informed choices that benefit your wallet and the environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the power consumption of a refrigerator?
The power consumption of a refrigerator can vary based on size, model, and usage. However, a typical refrigerator consumes around 150 to 250 watts.
How much energy does a washing machine use?
A washing machine's power consumption depends on the cycle and type of machine. A standard washing machine uses approximately 500 to 1500 watts.
What is the power consumption of a microwave oven?
Microwave ovens consume around 700 to 1200 watts. The power consumption depends on the microwave's wattage and usage time.
How much energy does a dishwasher use?
A dishwasher can consume between 1200 and 2400 watts. The specific power consumption depends on the cycle and the dishwasher's age and efficiency.
What is the power consumption of a television?
Televisions consume power even when turned off. A typical television uses around 50 to 100 watts.
How much energy does a ceiling fan use?
A ceiling fan consumes around 75 to 150 watts depending on the fan's size and speed.
How much energy does a computer use?
A desktop computer uses approximately 100 to 300 watts depending on its configuration and usage. A laptop typically consumes around 20 to 100 watts.
What is the power consumption of a laptop charger?
Laptop chargers consume around 20 to 40 watts depending on the charger's model.
How much energy does a hair dryer use?
A hair dryer consumes around 1000 to 2000 watts depending on its power level.
What is the power consumption of a toaster oven?
A toaster oven consumes around 1000 to 1500 watts depending on its size and power level.