Windmills vs. Wind Turbines: A Tale of Two Machines

The wind, a powerful force of nature, has been harnessed by humans for centuries. From the ancient windmills that ground grain to the modern wind turbines that power our homes, this natural resource has played a pivotal role in human history. While both windmills and wind turbines utilize the wind's energy, they differ significantly in their purpose, design, and scale.
Windmills: A Legacy of Mechanical Work
Windmills have a rich history, dating back over a millennium. The first documented windmills appeared in Persia around 800 C.E., where they were used to grind grain. These early windmills featured a simple design: a vertical axis with sails attached to a central shaft.
Windmills spread rapidly across Eurasia, becoming essential tools for agriculture and other industries. Throughout the 19th and 20th centuries, windmills were widely used for tasks like pumping water, grinding grain, and even sawing lumber. These machines were typically smaller than wind turbines, with blades often measuring around 8 feet in diameter. The wind's energy directly powered mechanical processes, making windmills indispensable for rural communities.
Wind Turbines: Modern Powerhouses of Electricity Generation
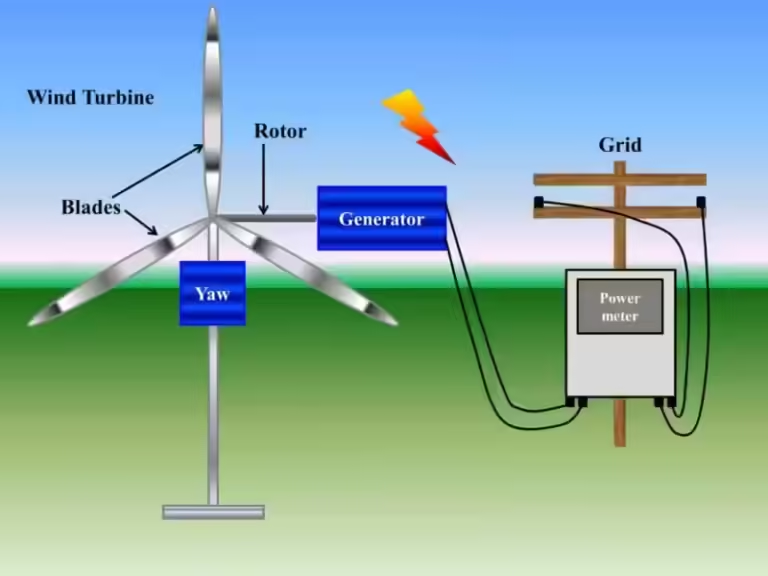
Wind turbines, on the other hand, are a relatively recent invention. The first wind turbine designed for electricity generation was constructed in 1888. This innovation marked a significant shift in the way wind energy was harnessed. Wind turbines use the wind's energy to rotate blades, which drive a generator to produce electricity. This process transforms wind energy into a form that can be used to power homes, businesses, and entire cities.
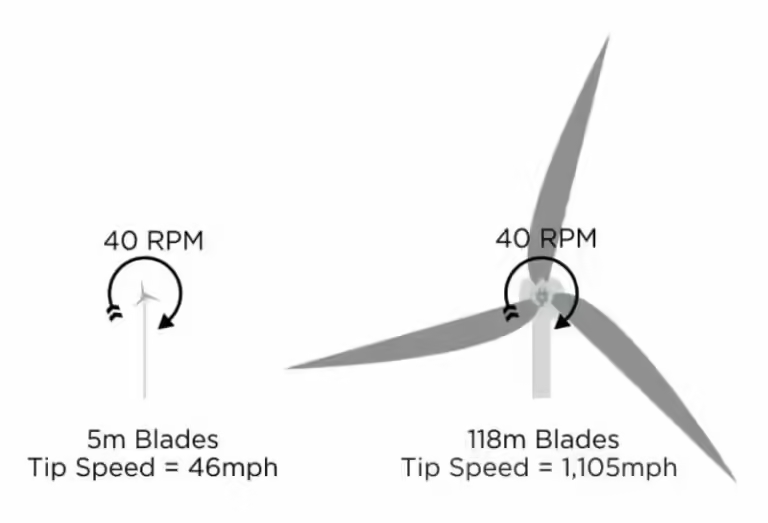
Unlike windmills, wind turbines are massive structures. Modern wind turbines can reach heights of around 280 feet, with blades exceeding 100 feet in length. These towering structures are designed to capture the maximum amount of wind energy, making them incredibly efficient at generating electricity. The horizontal axis design of wind turbines allows them to capture the wind's energy more effectively than windmills, leading to much higher power output.
Key Differences: A Comparative Overview
Here's a table summarizing the key differences between windmills and wind turbines:
| Feature | Windmill | Wind Turbine |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Mechanical work (e.g., grinding grain, pumping water) | Electricity generation |
| Size | Smaller, with blades around 8 feet in diameter | Larger, reaching heights of 280 feet with blades exceeding 100 feet |
| Design | Vertical axis | Horizontal axis |
| Technology | Simple mechanical design | Advanced technology for energy conversion |
A Glimpse into the Future of Wind Power
Both windmills and wind turbines have played crucial roles in shaping human history and harnessing the power of wind. While windmills represent a testament to the ingenuity of our ancestors, wind turbines are the future of wind energy. As technology continues to advance, we can expect wind turbines to become even more efficient and powerful, providing a clean and sustainable source of energy for generations to come.
From the ancient windmills that powered rural communities to the towering wind turbines that generate electricity for millions, the story of wind power is a testament to human ingenuity and our ongoing quest for sustainable energy solutions. As we look to the future, wind energy is poised to play an increasingly vital role in shaping a more sustainable and prosperous world.
Frequently Asked Questions about Windmills and Wind Turbines
What is the difference between a windmill and a wind turbine?
While both use wind, their purposes, designs, and scales differ. Windmills are older, mechanically driven machines for tasks like grinding grain or pumping water. Wind turbines are modern, generating electricity.
How do windmills and wind turbines differ in design?
Windmills typically have vertical blades rotating around a central shaft, while wind turbines have horizontal blades rotating around a central hub.
Which is larger, a windmill or a wind turbine?
Wind turbines are significantly larger, reaching heights of around 280 feet with blades exceeding 100 feet long. Windmills are typically much smaller.
What is the primary function of a windmill?
Windmills are primarily designed for mechanical work, using wind to power tasks like grinding grain or pumping water.
What is the primary function of a wind turbine?
Wind turbines are designed to generate electricity from wind. The rotating blades drive a generator, producing electricity.