The Burning Truth: A Simple Look at Fossil Fuel Combustion

Fossil fuels, like coal, oil, and natural gas, are the remnants of ancient lifeforms trapped beneath the Earth's surface for millions of years. These fuels, rich in carbon, hold a tremendous amount of stored energy. But what happens when we "burn" them?
The Chemistry of Combustion: A Simple Explanation
Burning fossil fuels is chemically similar to the natural process of oxidation, which happens all the time in nature. Imagine a piece of wood slowly rotting away. That's oxidation in action. In both cases, carbon atoms in the fuel combine with oxygen from the air, releasing energy.
The difference lies in the speed and intensity. When we burn fossil fuels, the reaction happens quickly, releasing a large amount of energy in the form of heat and light. This process is called combustion.
The Key Ingredients
Think of combustion like a recipe. You need three essential ingredients:
- Fuel: This is the substance that burns, like coal, oil, or natural gas.
- Oxygen: The air we breathe provides oxygen, which is crucial for the reaction to occur.
- Heat: You need an initial spark or flame to ignite the reaction, providing the energy to get things started.
This trio forms what we call the fire triangle. If any one of these is missing, the fire won't start or will quickly extinguish.
Breaking Down Fossil Fuel Combustion
When we burn fossil fuels, the carbon atoms within them react with oxygen from the air. This reaction creates two primary products:
- Carbon dioxide (CO2): This gas is a major greenhouse gas, trapping heat in the atmosphere and contributing to climate change.
- Water vapor (H2O): This is simply water in its gaseous form.
The burning of fossil fuels also releases other byproducts, including sulfur dioxide, a major contributor to acid rain, and nitrogen oxides, which form smog.
The Environmental Impact: Why We Need Alternatives
While burning fossil fuels provides us with energy, it comes at a significant cost to our planet.
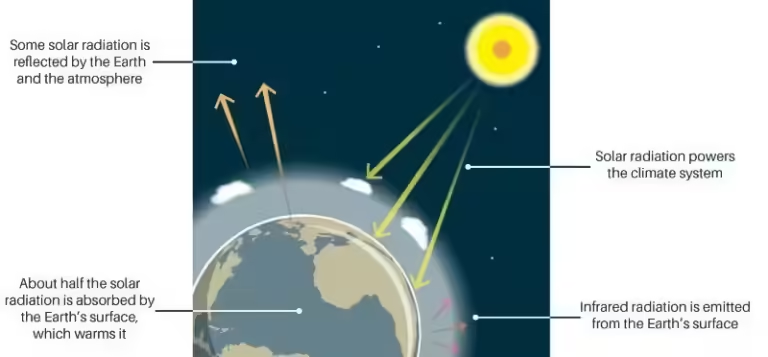
The release of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere is the primary driver of global warming. This trapped heat leads to:
- Rising sea levels
- More frequent and severe weather events
- Disruptions to ecosystems
- Increased health risks
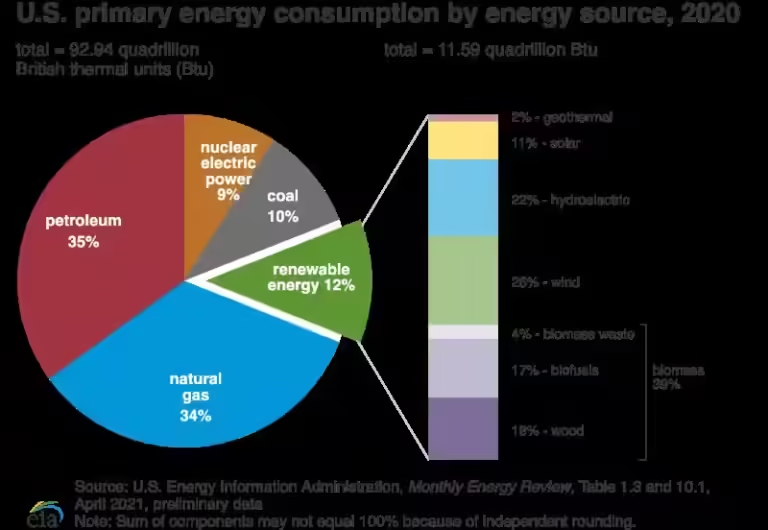
We must transition to cleaner energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydropower, to mitigate these harmful effects and protect our planet for future generations.
Frequently Asked Questions about Fossil Fuel Combustion
What is the chemical reaction involved in burning fossil fuels?
The chemical reaction involved is called combustion. It involves the combination of carbon atoms in the fossil fuel with oxygen from the air, creating carbon dioxide (CO2) and water vapor (H2O), releasing energy.
What are the three key ingredients needed for combustion?
They are fuel, oxygen, and heat. Think of it like a fire triangle.
What is the environmental impact of burning fossil fuels?
Burning fossil fuels releases carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere, a major contributor to climate change, trapping heat and causing global temperatures to rise.