All of the Following Are Greenhouse Gases Except: Unveiling the Mystery of Oxygen
The Earth's atmosphere is a complex and delicate system, vital for sustaining life. Within this atmosphere, certain gases play a crucial role in regulating our planet's temperature, acting like a blanket to trap heat. These gases are known as greenhouse gases. Their ability to absorb and re-emit infrared radiation, the type of radiation responsible for heat, leads to the greenhouse effect. However, not all atmospheric gases contribute to this warming phenomenon.
The Greenhouse Effect: A Blanket of Heat
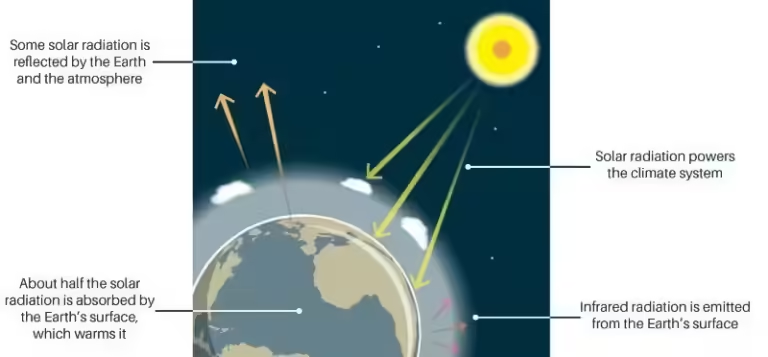
Imagine sunlight streaming through the Earth's atmosphere. Some of this energy is reflected back into space, while the rest is absorbed by the planet's surface, causing it to warm. This absorbed energy is then re-emitted as infrared radiation, radiating outward.
This is where greenhouse gases enter the picture. They act like a one-way mirror, allowing incoming sunlight to pass through but trapping the outgoing infrared radiation. This trapped heat contributes to the natural warming of the planet.
Think of it like a car parked under the sun. The windows allow sunlight to enter, warming the car's interior. But the glass prevents the heat from escaping, leading to a warm interior, even after the sun has set.
The Excluded Guest: Oxygen’s Role in the Atmosphere
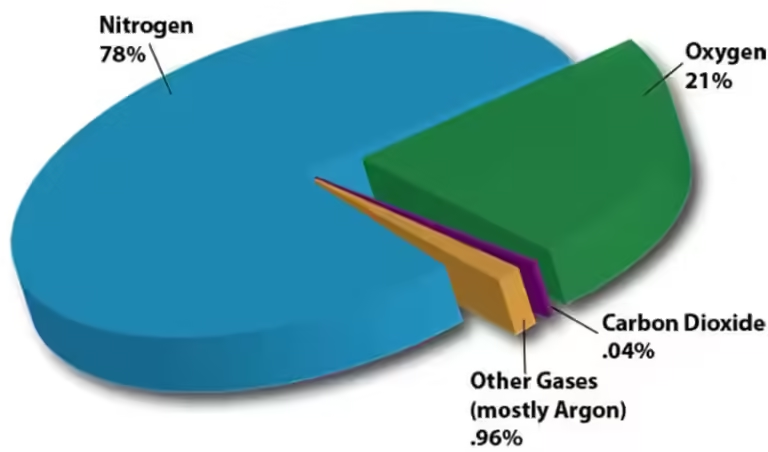
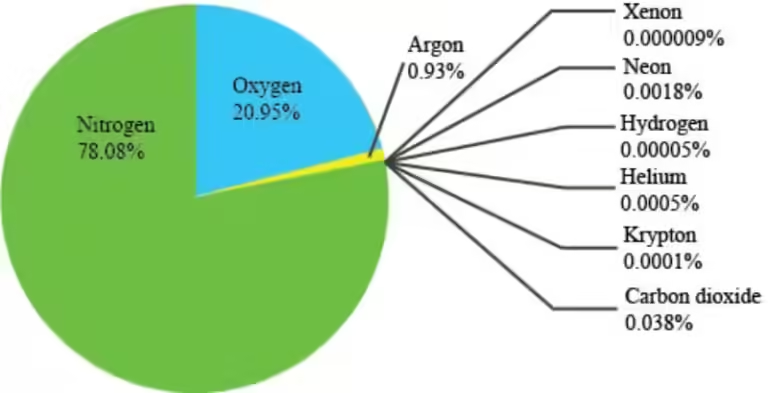
Now, let's dive into the question at hand: all of the following are greenhouse gases except? The answer, surprisingly, is oxygen (O2).
While oxygen is a vital component of our atmosphere, essential for respiration, it doesn't possess the molecular structure necessary to absorb and re-emit infrared radiation. It acts more like a bystander, allowing the greenhouse gases to do their work without participating in the process.
Oxygen plays a crucial role in other atmospheric processes, such as supporting combustion and forming ozone. However, when it comes to the greenhouse effect, it simply doesn't fit the bill.
Key Greenhouse Gas Players
To fully grasp the role of oxygen, it's essential to understand the significant players in the greenhouse effect:
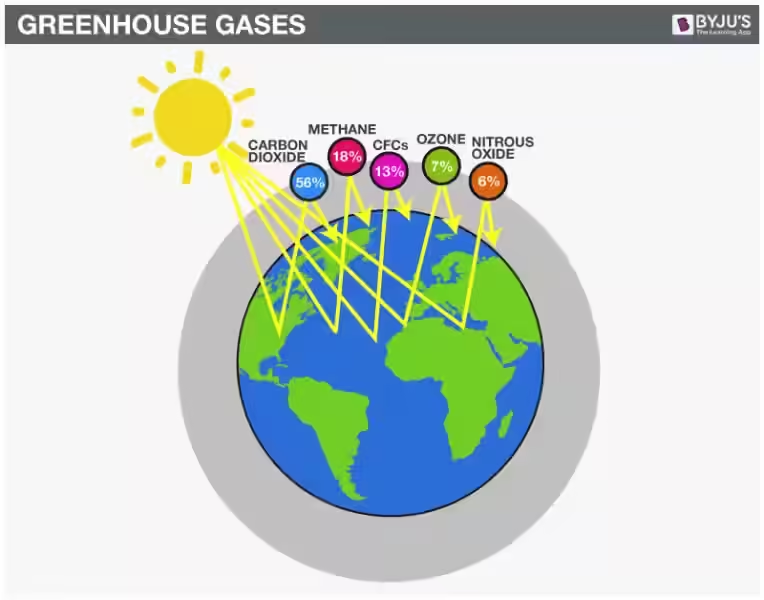
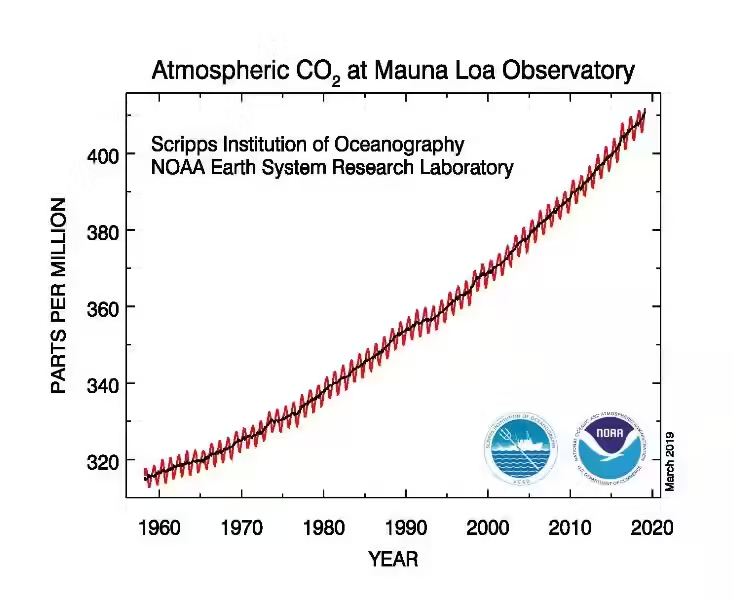
- Carbon dioxide (CO2): Released through natural processes like breathing and volcanic activity, carbon dioxide is a major contributor to the greenhouse effect. However, human activities, such as burning fossil fuels, are rapidly increasing its atmospheric concentration, intensifying the warming effect.
- Methane (CH4): A potent greenhouse gas, methane is released from sources like livestock, natural gas leaks, and decaying organic matter. Its trapping capacity is significantly higher than carbon dioxide, making it a major concern for climate change.
- Nitrous oxide (N2O): This gas is primarily released from agricultural activities, industrial processes, and the burning of fossil fuels. Its warming potential is even greater than methane, making it a significant factor in global warming.
- Water vapor (H2O): While often overlooked, water vapor is the most abundant greenhouse gas in the atmosphere. Its concentration fluctuates naturally with temperature and humidity, playing a complex role in climate feedback loops.
The Importance of Understanding Greenhouse Gases
So, why is it important to differentiate between oxygen and greenhouse gases? The answer lies in the urgency of addressing climate change. The increased concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere due to human activities is trapping more heat, leading to a warming planet with potentially devastating consequences.
By understanding the role of greenhouse gases and the unique properties of oxygen, we can better appreciate the delicate balance of our atmosphere and the urgency of mitigating climate change. This knowledge empowers us to make informed decisions and contribute to a more sustainable future for our planet.
Frequently Asked Questions
All of the following are greenhouse gases except?
Oxygen (O2) is not a greenhouse gas.