The Heart of Your Home: Understanding Your Gas Furnace
In the heart of your home, where warmth and comfort reside, lies a vital component: the gas furnace. This often-overlooked appliance works tirelessly to keep you cozy during the chilly months, silently humming away as it distributes warmth throughout your living space. But how does this seemingly simple machine achieve this feat? The answer lies in the intricate workings of the gas furnace, where combustion and heat transfer play crucial roles.
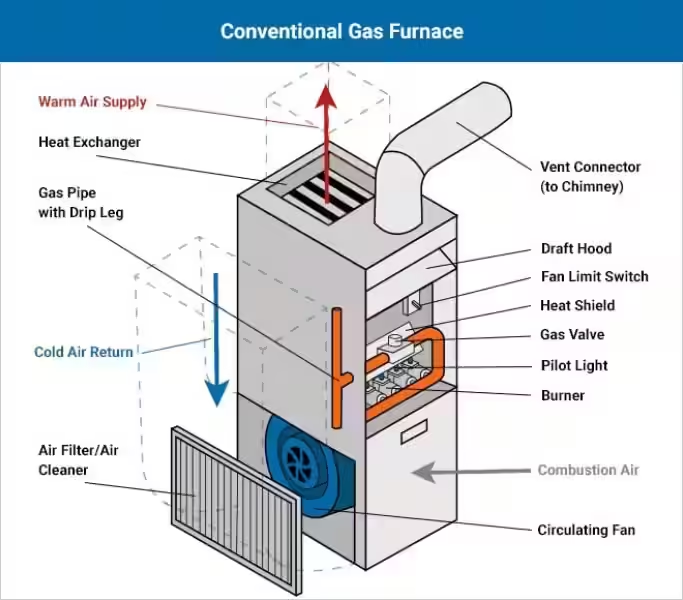
At the core of the gas furnace lies a burner, where natural gas is ignited, releasing a tremendous amount of heat. This heat is then transferred to a heat exchanger, a metal component designed to absorb the heat generated by the burning gas. The heat exchanger, often made of sturdy materials like aluminum or steel, is carefully constructed to efficiently transfer heat to the surrounding air.
The Journey of Warmth: How Heat is Distributed
The Power of Airflow: The Furnace's Lifeblood
Once the heat exchanger has absorbed the heat from the burning gas, the next step in the process involves distributing this warmth throughout your home. This is where the concept of airflow comes into play. Think of the furnace as a central hub, and the ductwork as a network of arteries, delivering warmth to every corner of your home. The furnace uses a powerful blower motor to pull air through the heat exchanger, where it is heated. This heated air is then pushed through the ductwork, ultimately reaching the vents and diffusers that release the warm air into your living spaces.
The efficiency of this process is critical for ensuring optimal heating performance. If there are leaks or blockages in the ductwork, the furnace may struggle to deliver adequate heat to all areas of your home. This can result in uneven heating, where some rooms are warmer than others, and a decrease in overall comfort.
A Symphony of Components: Ensuring Efficient Heat Transfer
The effective distribution of heat through your home relies on a carefully orchestrated interplay of various components. These components, working in harmony, ensure that the warmth generated by the furnace reaches its intended destination. Let's delve into some of these key players:
- Thermostat: This device acts as the brain of your heating system, controlling the furnace's operation by setting the desired temperature for your home. When the temperature drops below the set point, the thermostat signals the furnace to turn on, and vice versa.
- Ductwork: A network of pipes or tubes that carry the heated air from the furnace to various rooms in your home. Properly sized and insulated ductwork is crucial for minimizing heat loss and ensuring efficient distribution.
- Vents: Openings in walls or ceilings that allow the warm air from the ductwork to enter your living spaces. These vents should be strategically placed for optimal airflow and heat distribution.
- Diffusers: Devices that direct the airflow from the vents to create a comfortable and even temperature throughout the room. Well-designed diffusers can help prevent drafts and ensure that the warmth reaches every corner of the space.
By understanding how each component contributes to the overall system, you can gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate workings of your gas furnace. It's a testament to engineering ingenuity that a seemingly simple appliance can provide such a vital contribution to your comfort and well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions About Gas Furnaces
How does a gas furnace produce heat for distribution through a home?
A gas furnace uses natural gas or propane to heat air. The gas is burned in a combustion chamber, which generates hot gases. These hot gases are then transferred to a heat exchanger, where they warm the air. The heated air is then circulated throughout the home by a blower system.
What are the different types of gas furnaces?
There are several types of gas furnaces, including:
- Single-stage furnaces: These furnaces operate at a single heating capacity.
- Two-stage furnaces: These furnaces can operate at two different heating capacities, allowing for more precise temperature control.
- Modulating furnaces: These furnaces can adjust their heating output to match the home's heating needs, resulting in greater energy efficiency.
How does a gas furnace work?
A gas furnace works by burning fuel to heat air, which is then circulated throughout the home. The process involves the following steps:
- Gas supply: Natural gas or propane is delivered to the furnace through a gas line.
- Combustion: The gas is ignited in a combustion chamber, where it burns to produce heat.
- Heat transfer: The hot gases from the combustion chamber are transferred to a heat exchanger, which warms the air.
- Air circulation: The heated air is then circulated throughout the home by a blower system.
What are some common gas furnace problems?
Some common gas furnace problems include:
- Inadequate heat output: The furnace may not be able to heat the home adequately due to a problem with the system's efficiency or a blockage in the airflow.
- Unusual noises: The furnace may make strange sounds like banging, rattling, or screeching, which could indicate a problem requiring attention.
- Unusual smells: A gas furnace should not have a strong odor of gas. A strong, pungent smell could signal a leak, which is a serious safety hazard.
- Visible signs of damage: Any cracks, rust, or corrosion on the furnace or its components should be reported to a technician.
- Short cycling: If the furnace turns on and off frequently, it could mean there's a problem with the thermostat, airflow, or the system's efficiency.
What are some tips for maintaining a gas furnace?
Here are some tips for maintaining a gas furnace:
- Change the air filter regularly: A dirty air filter can restrict airflow and reduce the furnace's efficiency.
- Inspect the furnace annually: A qualified technician should inspect the furnace annually to ensure it's operating safely and efficiently.
- Clean the furnace: Cleaning the furnace regularly can help prevent dust and debris from accumulating and obstructing airflow.
- Seal any air leaks: Sealing any air leaks in the home can improve the furnace's efficiency and reduce heating costs.
How can I improve the energy efficiency of my gas furnace?
Here are some tips for improving the energy efficiency of a gas furnace:
- Install a programmable thermostat: A programmable thermostat can help you save energy by automatically adjusting the temperature settings based on your schedule.
- Upgrade to a high-efficiency furnace: High-efficiency furnaces use less energy to produce the same amount of heat.
- Seal any air leaks: Sealing any air leaks in the home can improve the furnace's efficiency and reduce heating costs.
- Insulate your home: Adding insulation to your attic and walls can help reduce heat loss and improve the furnace's efficiency.
- Use ceiling fans: Ceiling fans can help circulate warm air in the winter, reducing the need for the furnace to run as often.
What are some safety precautions to take when using a gas furnace?
Here are some safety precautions to take when using a gas furnace:
- Never use a gas furnace in an unventilated area.
- Have the furnace inspected annually by a qualified technician.
- Keep the area around the furnace clear of flammable materials.
- If you smell gas, evacuate the home immediately and call the gas company.
- Never attempt to repair a gas furnace yourself.
What are some common gas furnace safety issues?
Here are some common gas furnace safety issues:
- Carbon monoxide poisoning: Carbon monoxide is a colorless, odorless gas that can be deadly. A gas furnace that is not operating properly can produce carbon monoxide, so it is important to have the furnace inspected annually.
- Gas leaks: Gas leaks can be dangerous, so it is important to have the furnace inspected regularly.
- Fire hazards: A gas furnace that is not operating properly can be a fire hazard.
- Electrical hazards: A gas furnace can be an electrical hazard if it is not wired properly.
How can I prevent gas furnace safety issues?
Here are some tips for preventing gas furnace safety issues:
- Have the furnace inspected annually by a qualified technician.
- Keep the area around the furnace clear of flammable materials.
- Never use a gas furnace in an unventilated area.
- If you smell gas, evacuate the home immediately and call the gas company.
- Never attempt to repair a gas furnace yourself.