The Air We Breathe: A Deep Dive into Earth's Atmospheric Composition
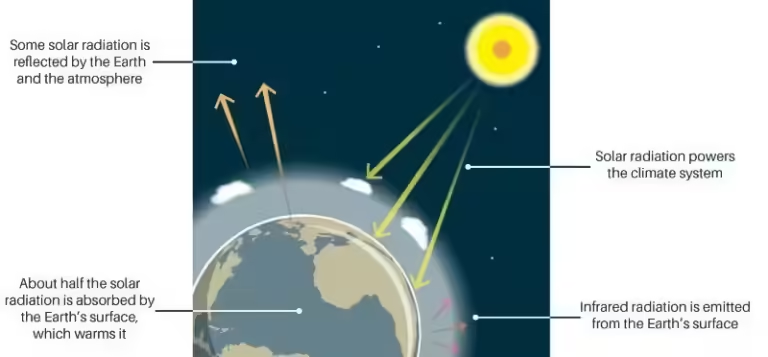
The Earth's atmosphere is an invisible shield, protecting us from harmful radiation from the Sun and providing the air we need to survive. But have you ever wondered what exactly makes up this blanket of air that surrounds our planet? It's a fascinating mix of different gases, each with its own unique properties and roles.
Nitrogen: The Silent Majority
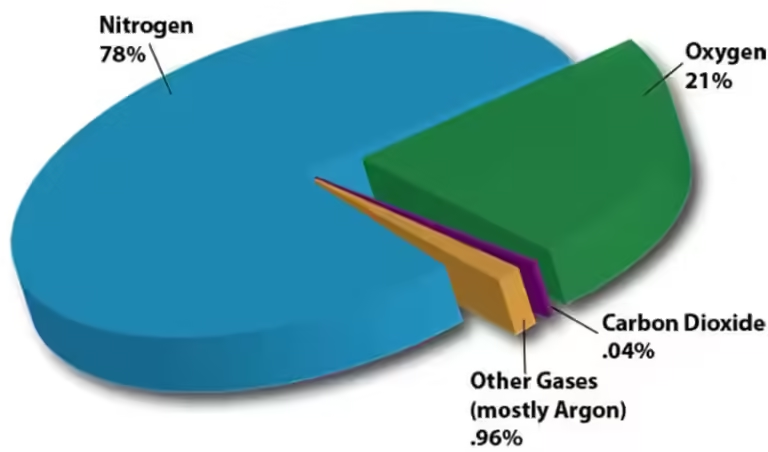
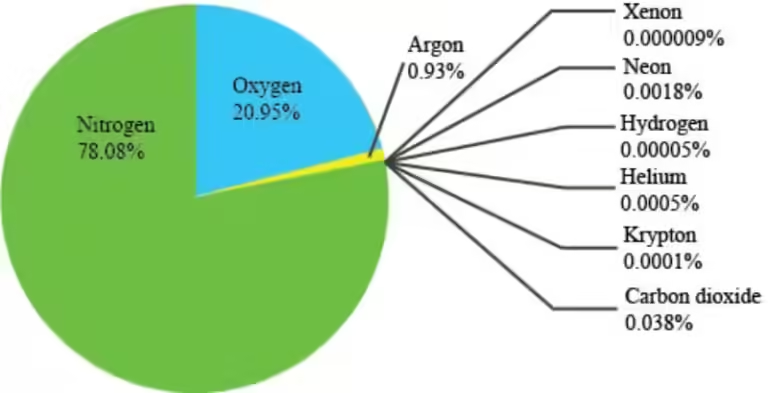
Nitrogen, a colorless, odorless, and largely unreactive gas, makes up a whopping 78% of our atmosphere. It's the most abundant gas, silently existing without much fanfare. While nitrogen is essential for life, it's not directly usable by most organisms. Think of it like a locked treasure chest; it needs to be unlocked before its valuable contents can be used. This unlocking process is called nitrogen fixation, where nitrogen is converted into usable forms like nitrates by certain bacteria and other biological processes.
Oxygen: The Life-Giving Gas
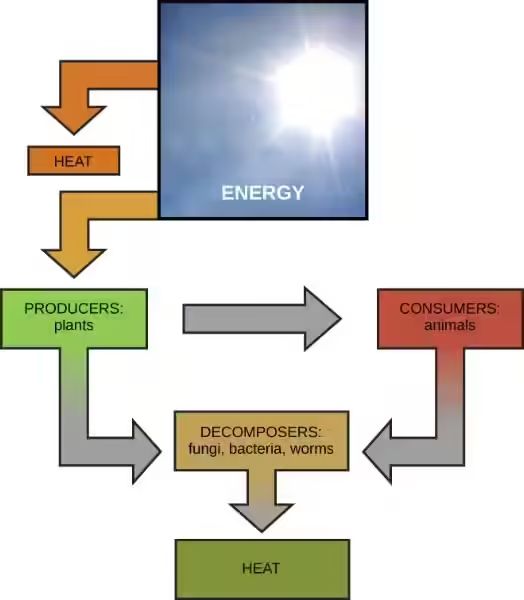
Oxygen, the second most abundant gas at 21%, is the star of the show. It's the key ingredient for respiration, the process by which organisms convert food into energy. Without oxygen, life as we know it wouldn't exist. Plants and algae are the heroes of this story, producing oxygen as a byproduct of photosynthesis. It's a beautiful cycle—plants use carbon dioxide and sunlight to make food, releasing oxygen in the process, while animals breathe in oxygen and exhale carbon dioxide, providing the raw materials for plants to continue the cycle.
Argon: The Silent Partner
Argon is a noble gas, meaning it's very stable and doesn't easily react with other substances. It makes up the remaining 0.9% of our atmosphere, playing a more passive role in the grand scheme of things. It's like the quiet friend who is always present but rarely takes center stage.
Trace Gases: A World of Impact
While nitrogen, oxygen, and argon dominate the atmosphere, other gases, present in much smaller amounts, are crucial for various processes. These are often referred to as trace gases.
Carbon Dioxide: A Double-Edged Sword
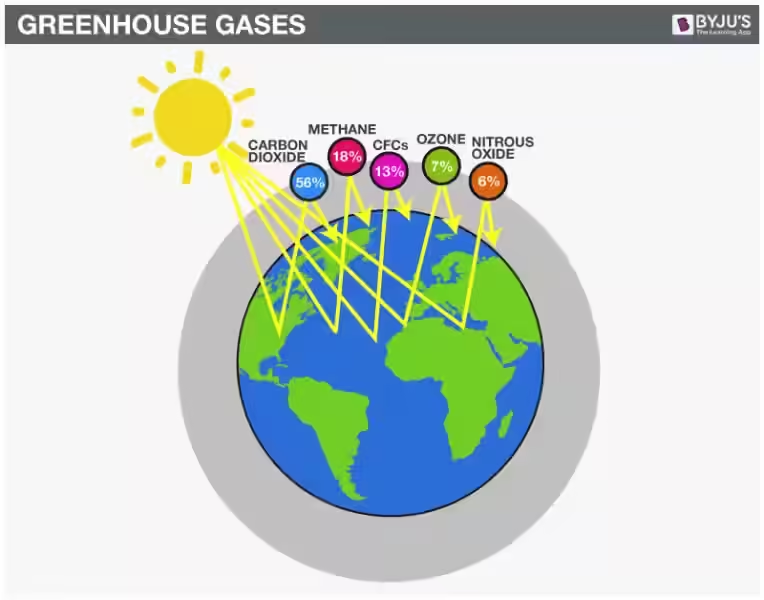
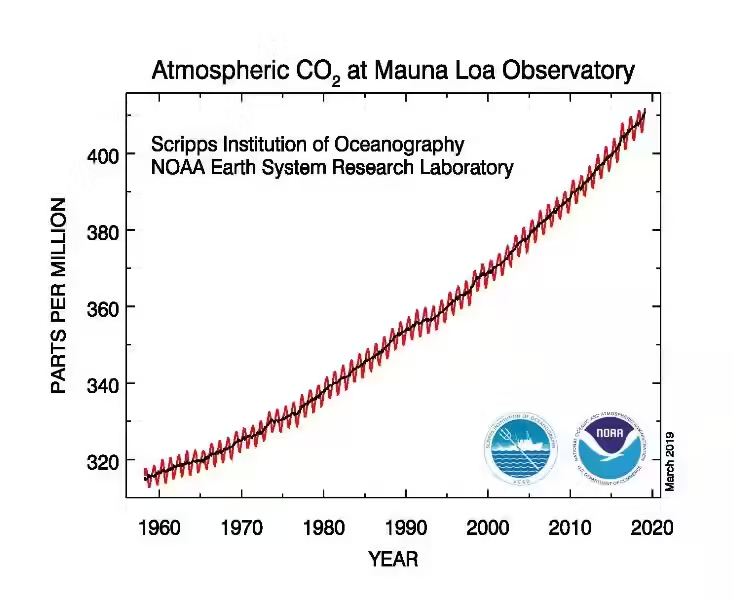
Carbon dioxide (CO2), though present in small amounts, is a powerful greenhouse gas. It traps heat in the atmosphere, helping to keep our planet warm enough for life to thrive. However, human activities like burning fossil fuels are increasing CO2 levels, leading to a phenomenon known as climate change. This imbalance can have significant consequences, including rising global temperatures, extreme weather events, and rising sea levels.
Other Important Trace Gases
Neon, helium, methane, krypton, hydrogen, and ozone are all present in trace amounts but play essential roles in various atmospheric processes. Ozone (O3), for instance, forms a protective layer in the stratosphere, shielding us from harmful ultraviolet radiation from the Sun.
Water Vapor: The Dynamic Element
Water vapor (H2O), while not a permanent constituent of the atmosphere, is crucial for weather patterns and cloud formation. Its presence varies depending on location and time, making it a dynamic element in the atmosphere.
A Symphony of Gases
Understanding the composition of the Earth's atmosphere is crucial for comprehending the complex interactions that influence our planet's climate, weather patterns, and life itself. The presence of these gases, their relative abundance, and their interactions create a dynamic system that is constantly changing.
In conclusion, the most abundant gases in Earth's atmosphere are nitrogen (78%), oxygen (21%), and argon (0.9%). While these gases form the foundation of our atmosphere, trace gases like carbon dioxide, water vapor, and others play crucial roles in regulating climate, weather, and life processes. Recognizing the importance of this delicate balance and understanding the impact of human activities on the atmosphere is essential for safeguarding the health of our planet and ensuring a future for all living things.
Frequently Asked Questions
What gas is the most abundant in the atmosphere?
Nitrogen.