Which of the following statements is true of green grass?

Green grass is a sight that brings joy to many. It evokes feelings of peace, tranquility, and a connection to nature. But have you ever stopped to ponder the science behind this familiar sight? Green grass isn't just a simple shade of green; it's a testament to the complex interplay of light, pigments, and the very essence of life.
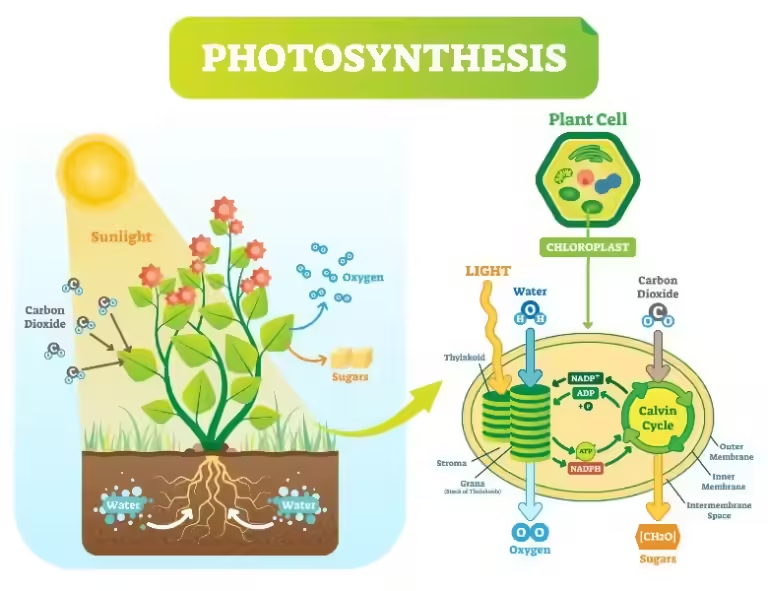
The vibrant green color of grass is not due to a single pigment, but rather a combination of several. The most prominent of these is chlorophyll, the pigment that makes plants green. Chlorophyll is responsible for absorbing light energy from the sun, which plants use for photosynthesis, the process of converting light energy into chemical energy. Without chlorophyll, plants would not be able to survive.
The Role of Chlorophyll in Green Grass
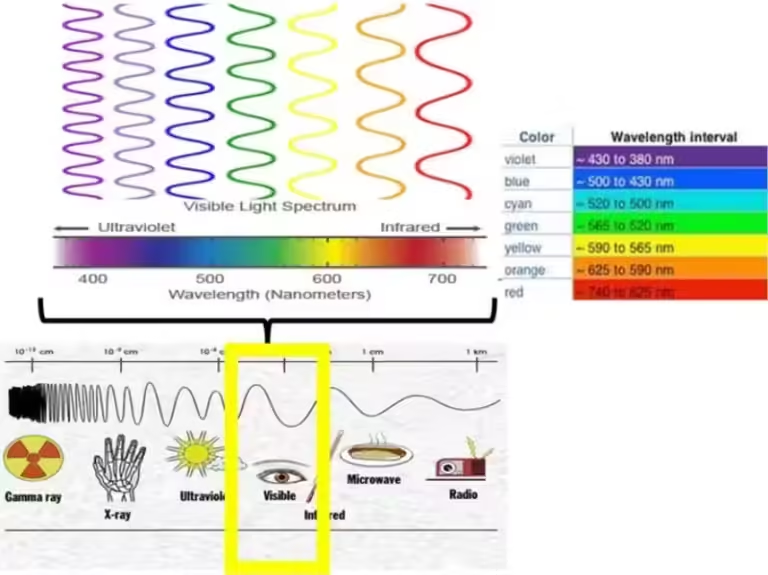
Chlorophyll is a complex molecule that absorbs light in the red and blue wavelengths of the visible spectrum, but it reflects green light. This reflected green light is what we see as the color of grass. Chlorophyll is essential for photosynthesis, as it captures light energy that plants use to produce sugars, which provide them with the energy they need to grow and thrive.
The amount of chlorophyll in grass can vary depending on factors such as the season, the amount of sunlight, and the type of grass. In the spring and summer, when there is plenty of sunlight, grass typically has more chlorophyll and appears a brighter green. In the fall and winter, when there is less sunlight, grass produces less chlorophyll and may appear a more yellowish-green.
Other Pigments Contributing to Grass’s Color
While chlorophyll is the primary pigment responsible for the green color of grass, other pigments also play a role. These pigments can contribute to the overall color of grass, making it appear slightly different shades of green or even yellow, depending on the variety of grass and the environmental factors.
Some examples of other pigments found in grass include carotenoids, which are responsible for the yellow and orange colors of carrots and other fruits and vegetables. Carotenoids are also present in grass, but in much smaller amounts than chlorophyll. These pigments can contribute to the overall yellowness of grass, especially in the fall when chlorophyll production declines.
The Importance of Light for Grass’s Color
The amount of light that grass receives also plays a crucial role in its color. Grass that is exposed to ample sunlight will have more chlorophyll and appear a brighter green. On the other hand, grass that is shaded or grows in low light conditions will have less chlorophyll and may appear a paler green or even yellow.
This is why you often see a difference in the color of grass in different parts of a lawn. Grass that receives direct sunlight will be a brighter green than grass that is shaded by trees or buildings. The amount of light that grass receives is one of the factors that determines its overall health and vigor.
The Importance of Water for Grass’s Health
Water is essential for grass to maintain its healthy green color. Water is used in photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy. Without enough water, grass will wilt and eventually die.
When grass is dehydrated, it loses its turgor pressure, which is the pressure that keeps the grass blades upright. As a result, the blades will droop and become limp. The grass may also turn a yellowish-brown color as it loses chlorophyll.
Which of the following statements is true of green grass?
The true statement about green grass is that it's a complex combination of pigments and factors, including chlorophyll, light, and water. It's not simply green because of one specific pigment or reason. Green grass is a vibrant testament to the intricate processes that sustain life on Earth.
Frequently Asked Questions about Green Grass
What is the primary function of green grass?
The primary function of green grass is photosynthesis, which is the process of converting sunlight into energy.
Why is green grass green?
Green grass is green because it contains chlorophyll, a pigment that absorbs sunlight for photosynthesis. Chlorophyll absorbs all colors except green, which is reflected back, making the grass appear green.
What are the benefits of green grass?
Green grass provides several benefits, including:
- Aesthetic appeal: Green grass adds beauty and natural appeal to landscapes.
- Erosion control: Grass roots bind soil together, preventing erosion.
- Air purification: Grass absorbs carbon dioxide and releases oxygen, contributing to air quality.
- Habitat for wildlife: Grass provides a habitat for various insects, birds, and small mammals.
How do I care for green grass?
Caring for green grass involves:
- Watering: Providing sufficient water to maintain healthy growth.
- Mowing: Regularly cutting the grass to maintain a desired height.
- Fertilizing: Adding nutrients to the soil to support growth.
- Weed control: Removing unwanted plants that compete with grass.
What are some common problems faced by green grass?
Common problems include:
- Disease: Grass can be affected by various diseases caused by fungi, bacteria, or viruses.
- Pests: Insects and other pests can damage grass.
- Drought: Lack of water can cause grass to wilt and die.
- Over-fertilization: Too much fertilizer can burn grass.
What are some of the different types of green grass?
There are many types of green grass, each with its own unique characteristics. Some popular types include:
- Kentucky bluegrass: A cool-season grass known for its durability and dark green color.
- Bermuda grass: A warm-season grass that thrives in hot climates.
- Fescue: A cool-season grass that tolerates shade and drought.
- Ryegrass: A cool-season grass that grows quickly and provides good winter cover.