The Greenhouse Effect: A Human-Induced Phenomenon
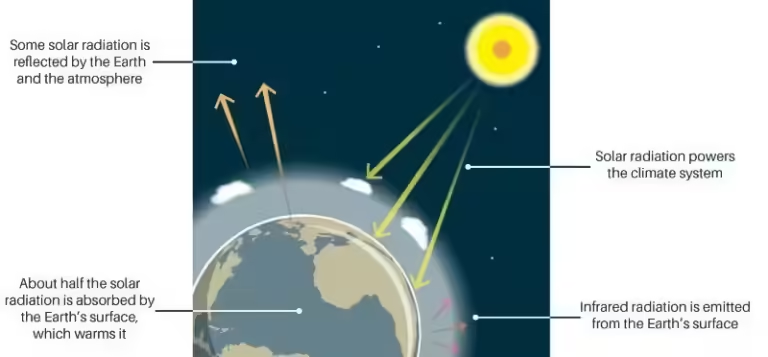
The Earth's atmosphere naturally traps heat from the sun, keeping our planet warm enough to support life. This process, known as the greenhouse effect, is essential for life as we know it. However, human activities are significantly amplifying the greenhouse effect, leading to a dramatic increase in global temperatures, a phenomenon known as global warming.
Think of the greenhouse effect as a blanket that keeps the Earth warm. The sun's rays penetrate the atmosphere and warm the Earth's surface. As the Earth radiates this heat back into space, certain gases in the atmosphere, known as greenhouse gases, trap some of that heat. This trapped heat keeps the planet warm. While this is a natural process, human activities are releasing excessive amounts of these greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, thickening the blanket and causing the Earth to warm up more than it should.
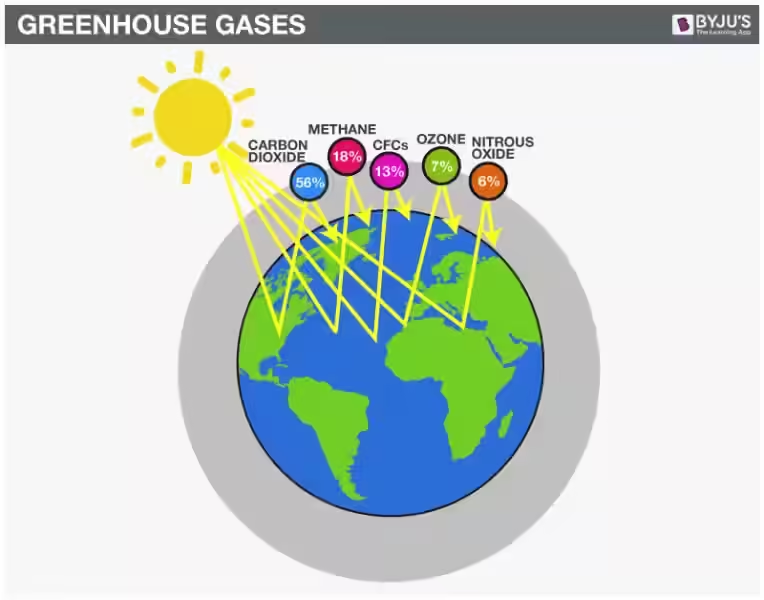
The Culprits: Greenhouse Gases
Several gases contribute to the greenhouse effect, but some are more potent than others. Carbon dioxide (CO2) is the most prevalent greenhouse gas, primarily released from burning fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas. Methane (CH4), emitted from livestock, agriculture, and natural gas leaks, is another major contributor. Nitrous oxide (N2O), largely linked to agricultural activities, is a potent greenhouse gas, trapping much more heat than CO2. Other greenhouse gases, including fluorinated gases used in refrigerators and air conditioners, also play a significant role.
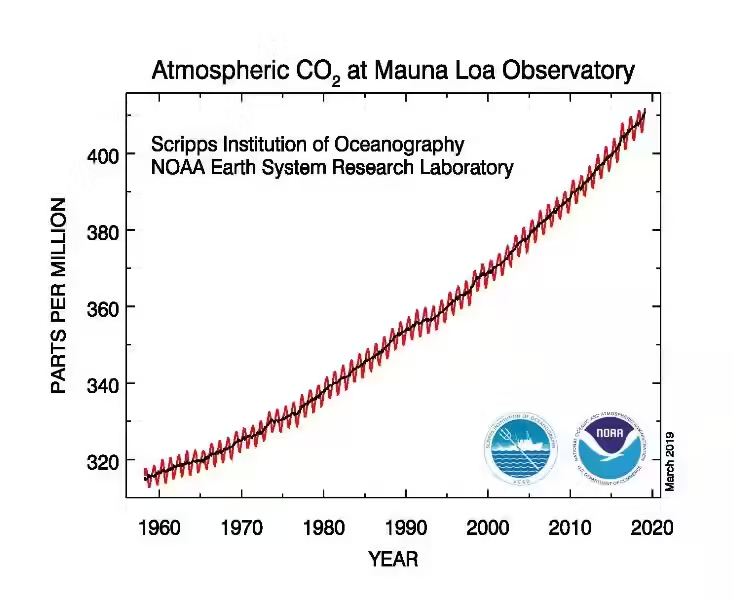
The problem isn't just the presence of these gases but their increased concentration in the atmosphere. Human activities are releasing these gases at an unprecedented rate, overwhelming the natural processes that remove them from the atmosphere. This imbalance is the primary driver of the amplified greenhouse effect and subsequent global warming.
Fossil Fuel Consumption: The Main Driver
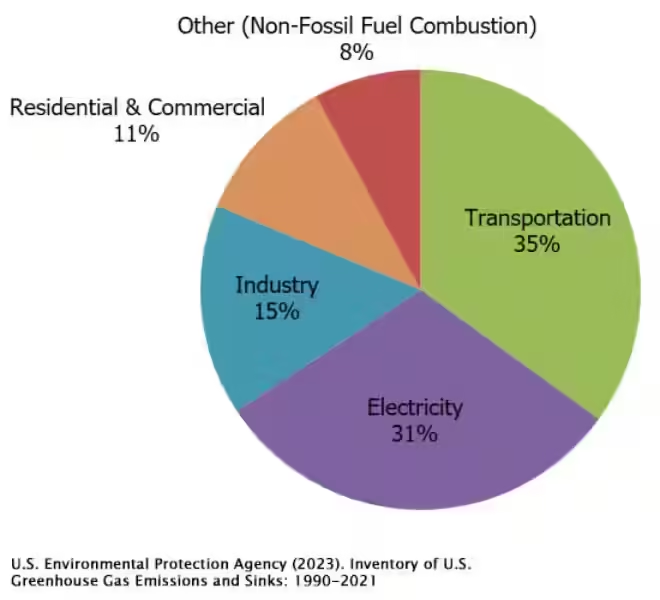
Fossil fuels power our modern world. From electricity generation to transportation, we rely heavily on these energy sources. However, the burning of fossil fuels releases vast amounts of CO2 into the atmosphere, accounting for the majority of human-induced greenhouse gas emissions. As global energy demand continues to rise, so too will the reliance on fossil fuels, exacerbating the problem.
The energy sector is responsible for about three-quarters of global CO2 emissions, highlighting the urgent need to transition to cleaner energy sources. Renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydropower offer a viable alternative to fossil fuels, reducing our reliance on these greenhouse gas-emitting sources.
Deforestation: A Double Whammy
Forests play a crucial role in mitigating the greenhouse effect. They act as carbon sinks, absorbing CO2 from the atmosphere through photosynthesis. However, deforestation is removing these vital carbon sinks, releasing stored CO2 back into the atmosphere and further amplifying the greenhouse effect.
Deforestation for agriculture, logging, and urbanization is a major contributor to increased CO2 emissions. The loss of forests not only reduces carbon absorption but also limits the natural processes that remove existing CO2 from the atmosphere. Protecting and restoring forests is crucial for mitigating climate change.
The Consequences of a Warming Planet
The amplified greenhouse effect is not a theoretical problem; its consequences are already being felt around the world. Rising global temperatures are leading to more extreme weather events, such as heatwaves, droughts, floods, and hurricanes. These events have devastating implications for human health, infrastructure, and ecosystems.
Rising sea levels due to melting glaciers and ice sheets threaten coastal communities and infrastructure. Ocean acidification, caused by the absorption of increased CO2, threatens marine life and ecosystems. Changes in agricultural yields due to shifting climate patterns pose a threat to food security. These are just a few examples of the far-reaching consequences of the amplified greenhouse effect.
The Need for Urgent Action
The scientific consensus is clear: the greenhouse effect is being amplified by human activity, and the consequences are severe. A rapid transition to a low-carbon economy is essential to mitigate the worst effects of climate change. This requires a global effort to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, develop sustainable technologies, and adapt to the changing climate.
Individual actions can also make a difference. Conserving energy, reducing our reliance on fossil fuels, supporting sustainable businesses, and advocating for climate action are crucial steps in mitigating the amplified greenhouse effect. The future of our planet depends on our collective commitment to tackling this pressing challenge.
Frequently Asked Questions About the Greenhouse Effect
Is the greenhouse effect caused solely by human activity?
No, the greenhouse effect is a natural process that has been occurring for millions of years. It is essential for life on Earth, as it traps some of the Sun's heat and keeps the planet warm enough to support life.
What is the role of human activity in the greenhouse effect?
While the greenhouse effect is natural, human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels, have significantly increased the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. This has led to a more pronounced greenhouse effect, resulting in global warming.