The Greenhouse Effect: A Natural Blanket Keeping Our Planet Warm

A Vital Process for Life on Earth
Imagine our planet without the warmth of the sun. It would be a frozen wasteland, incapable of supporting life as we know it. The greenhouse effect refers to the process by which certain gases in the Earth's atmosphere trap heat from the sun, keeping our planet warm enough for life to thrive.
Think of it like a blanket on a cold night. The blanket traps your body heat, keeping you warm. Similarly, the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere trap heat from the sun, warming the Earth's surface. This process is essential for maintaining a stable climate that allows plants, animals, and humans to flourish.
How the Greenhouse Effect Works
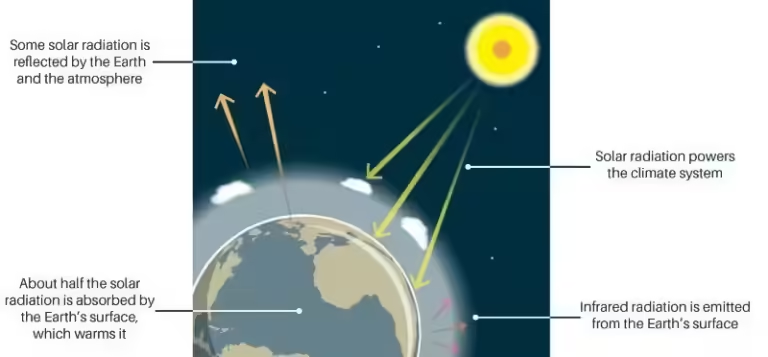
The sun's energy reaches the Earth in the form of radiation. Some of this radiation is reflected back into space, while the rest is absorbed by the Earth's surface, warming it. As the Earth's surface warms, it emits infrared radiation, which is a type of heat energy.
This is where the greenhouse gases come in. These gases act like a one-way mirror, allowing sunlight to pass through but trapping the outgoing infrared radiation. This trapped heat warms the atmosphere and the Earth's surface, creating the planet's average temperature.
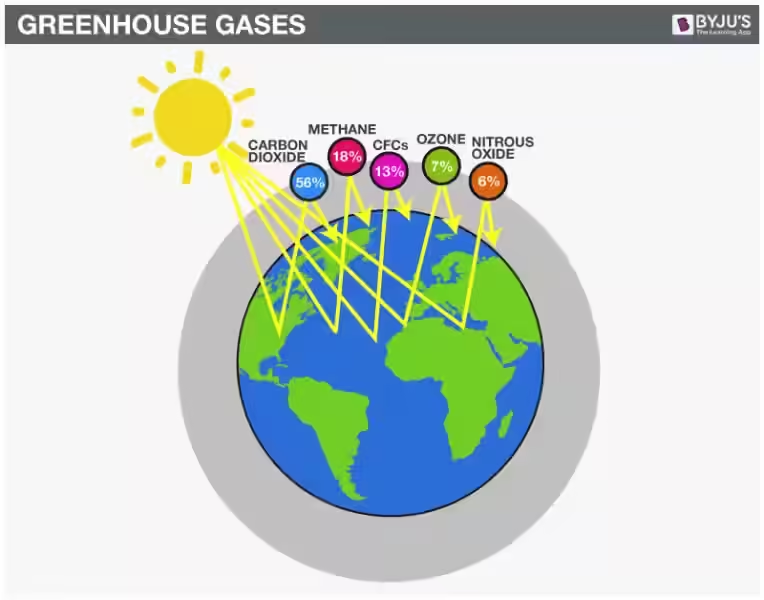
The Key Players: Greenhouse Gases
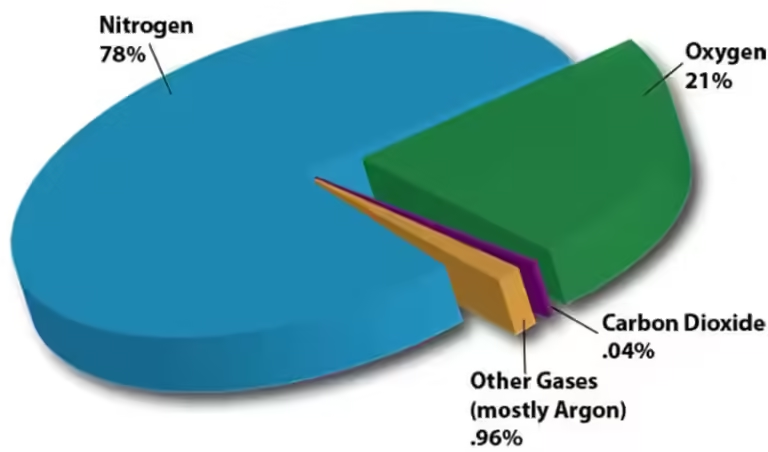
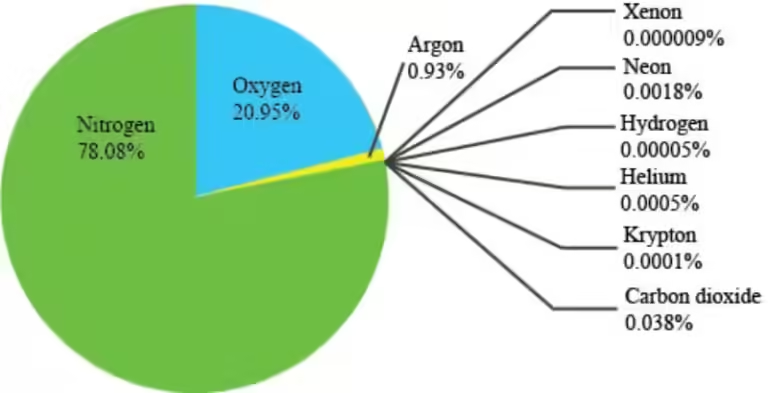
The most important greenhouse gases include:
- Carbon dioxide (CO2): Released from burning fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes.
- Methane (CH4): Released from livestock, natural gas leaks, and waste decomposition.
- Nitrous oxide (N2O): Released from agricultural activities, industrial processes, and burning fossil fuels.
- Fluorinated gases: Used in refrigeration, air conditioning, and industrial processes.
While these gases are naturally present in the atmosphere, human activities have significantly increased their concentrations, leading to an enhanced greenhouse effect and a warming planet.
A Natural Phenomenon with a Human Twist
The greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon that has played a critical role in shaping our planet's climate throughout history. However, human activities have altered this delicate balance, leading to a heightened greenhouse effect and climate change.
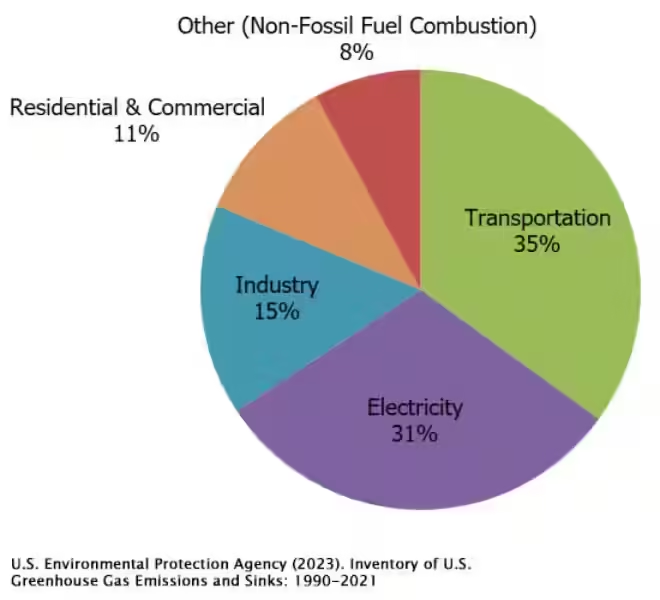
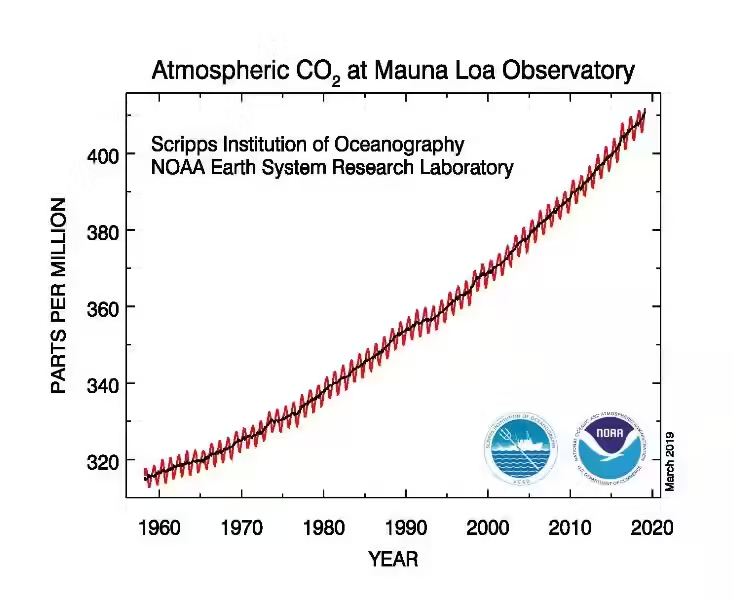
Since the Industrial Revolution, humans have been releasing vast amounts of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, primarily through burning fossil fuels for energy and industrial processes. This has led to a significant increase in the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, trapping more heat and causing the Earth's average temperature to rise.
The Consequences of a Warmer Planet
The consequences of a warmer planet are far-reaching and potentially devastating. These include:
- Rising sea levels: Melting glaciers and ice sheets contribute to rising sea levels, threatening coastal communities and ecosystems.
- Extreme weather events: More frequent and intense heat waves, droughts, storms, and floods.
- Changes in plant and animal life: Shifting habitats and species extinction as ecosystems struggle to adapt to changing conditions.
- Impacts on human health: Increased heat-related illnesses, respiratory problems, and vector-borne diseases.
- Economic and social disruptions: Displaced populations, food shortages, and conflicts over resources.
Mitigating the Impact of Climate Change
The scientific consensus is clear: human activities are driving climate change, and we must take action to mitigate its impacts. This requires a global effort to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and transition towards a sustainable future.
Here are some key strategies:
- Transition to renewable energy sources: Wind, solar, and hydropower are cleaner alternatives to fossil fuels.
- Improve energy efficiency: Reducing energy consumption through better building insulation, more efficient appliances, and public transport.
- Sustainable agriculture and forestry: Protecting forests, promoting sustainable farming practices, and reducing deforestation.
- Carbon capture and storage: Developing technologies to capture and store carbon dioxide emissions.
- International cooperation: Global agreements and partnerships are crucial for tackling this global challenge.
By understanding the greenhouse effect and its role in climate change, we can make informed decisions to protect our planet and ensure a healthy future for generations to come. The challenge is significant, but with collective effort and innovation, we can build a more sustainable future and preserve the Earth's delicate balance for generations to come.
Frequently Asked Questions about the Greenhouse Effect
What is the greenhouse effect?
The greenhouse effect is the process by which certain gases in the Earth's atmosphere trap heat from the sun.
What are the main greenhouse gases?
The main greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and fluorinated gases.
How does the greenhouse effect work?
When sunlight reaches Earth, some of it is reflected back into space, while the rest is absorbed by the planet's surface. This absorbed energy warms the Earth. As the Earth warms, it radiates infrared energy back into the atmosphere. Greenhouse gases absorb this infrared radiation, trapping heat in the atmosphere and warming the planet.
Why is the greenhouse effect important?
The greenhouse effect is a natural process that is essential for life on Earth. Without it, our planet would be too cold to support life.
What is the difference between the natural greenhouse effect and the enhanced greenhouse effect?
The natural greenhouse effect is a naturally occurring process that keeps the Earth warm enough to support life. The enhanced greenhouse effect, also known as global warming, is caused by human activities that release additional greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, trapping more heat and warming the planet at an accelerated rate.
What are the effects of the enhanced greenhouse effect?
The enhanced greenhouse effect is causing a number of changes to the Earth's climate, including rising global temperatures, changes in precipitation patterns, more extreme weather events, and rising sea levels.
What can we do to reduce the enhanced greenhouse effect?
There are many things we can do to reduce our impact on the climate, including reducing our reliance on fossil fuels, improving energy efficiency, and supporting policies that promote renewable energy sources.